Wound repair in rabbits using autologous biomaterials combined with rosuvastatin
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1590/1809-6891v26e-78752EAbstract
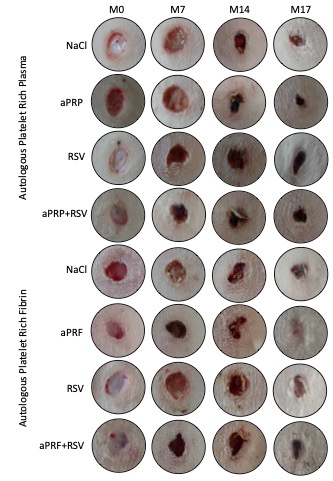
Autologous platelet-rich plasma (aPRP) and autologous platelet-rich fibrin (aPRF) are blood-derived biomaterials that potentially enhance wound healing. Rosuvastatin (RSV), a lipidlowering statin, exhibits pleiotropic effects that may promote tissue repair, warranting investigation into its use alone or combined with biomaterials for wound healing. This study aims to evaluate the wound repair effects of aPRP and aPRF, with or without adding 1.2% rosuvastatin. Sixteen clinically healthy adult male New Zealand rabbits were randomly assigned to two groups of eight, each receiving one of the biomaterials either with or without 1.2% rosuvastatin. The biomaterials used were of autologous origin, specifically aPRP and aPRF. Surgical wounds were induced and treated with biomaterials and 1.2% rosuvastatin over 17 days. Macroscopic assessments of wound area and epithelial gap distance were conducted, supplemented by histological analysis. A significant inverse correlation was observed between wound area and epithelial thickness with the use of aPRF (r = -0.5500). No significant difference was found in epithelial thickness between treatment groups (p > 0.05). In terms of the wound area, aPRP alone (p = 0.001), aPRF alone (p = 0.021), and aPRP+RSV (p = 0.016) treatments yielded smaller wound areas compared to aPRF+RSV at 14 days post-treatment. These findings suggest that the addition of 1.2% rosuvastatin to aPRP resulting in a smaller wound area compared to aPRF, enhances wound repair.
Downloads
References
Gurtner GC, Werner S, Barrandon Y, Longaker MT. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature. 2008;453(7193):314-321. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07039
Pastar I, Stojadinovic O, Yin NC, Ramirez H, Nusbaum AG, Sawaya A, et al. Epithelialization in wound healing: a comprehensive review. Adv Wound Care. 2014;3(7):445-464. https://doi.org/10.1089/wound.2013.0473
Roy S, Driggs J, Elgharably H, Biswas S, Findley M, Khanna S, et al. Platelet‐rich fibrin matrix improves wound angiogenesis via inducing endothelial cell proliferation. Wound Repair Regen. 2011;19(6):753-766. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-475X.2011.00740.x.
Hermeto LC, Rossi RD, Pádua SBD, Pontes ERJ, Santana AE. Comparative study between fibrin glue and platelet rich plasma in dogs skin grafts. Acta Cir Bras. 2012;27:789-794. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-86502012001100008
Desai CB, Mahindra UR, Kini YK, Bakshi MK. Use of platelet-rich fibrin over skin wounds: Modified secondary intention healing. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2013;6(1):35. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-2077.110096
Ehrenfest DMD, Andia I, Zumstein MA, Zhang CQ, Pinto NR, Bielecki T. Classification of platelet concentrates (Platelet-Rich Plasma-PRP, Platelet-Rich Fibrin-PRF) for topical and infiltrative use in orthopedic and sports medicine: current consensus, clinical implications and perspectives. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014;4(1):3. (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4049647/)
Prakash S, Thakur A. Platelet concentrates: past, present and future. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2011;10(1):45-49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-011-0182-4
Sanchez-González DJ, Méndez-Bolaina E, Trejo-Bahena NI. Platelet-rich plasma peptides: key for regeneration. Int J Pept. 2012;2012:532519. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/532519
Barrionuevo DV, Laposy CB, Abegão KGB, Nogueira RMB, Nai GA, Bracale BN, et al. Comparison of experimentally-induced wounds in rabbits treated with different sources of platelet-rich plasma. Lab Anim. 2015;49(3):209-214. https://doi.org/10.1177/0023677214567747
Ferreira NGO, Vicentini YF, Breda MRS, Nogueira RMB, Nai GA, Santarém CL. Uso de biomateriais e rosuvastatina tópica aumenta angiogênese de feridas cirúrgicas em coelhos. Res Soc Dev. 2021;10(1). https://doi.org/10.33448/rsd-v10i1.11327
Bao JW, Sun B, Ma PP, Gai YS, Sun WZ, Yu HQ, et al. Rosuvastatin inhibits inflammatory response and resists fibrosis after myocardial infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(1). https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201801_14123
Pradeep AR, Karvekar S, Nagpal K, Patnaik K, Guruprasad CN, Kumaraswamy KM. Efficacy of locally delivered 1.2% rosuvastatin gel to non‐surgical treatment of patients with chronic periodontitis: A randomized, placebo‐controlled clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2015;86(6):738-745. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2015.140631
Asai J, Takenaka H, Hirakawa S, Sakabe JI, Hagura A, Kishimoto S, et al. Topical simvastatin accelerates wound healing in diabetes by enhancing angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2012;181(6):2217-2224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.08.023
Salem, H.F.; Nafady, M.M.; Ewees, M.G.E.-D.; Hassan, H.; Khallaf, R.A. Rosuvastatin calcium-based novel nanocubic vesicles capped with silver nanoparticles-loaded hydrogel for wound healing management: Optimization employing Box–Behnken design: In vitro and in vivo assessment. J. Liposome Res. 2022, 32, 45–61. https://doi.org/10.1080/08982104.2020.1867166
Aly, U.F.; Abou-Taleb, H.A.; Abdellatif, A.A.; Tolba, N.S. Formulation and evaluation of simvastatin polymeric nanoparticles loaded in hydrogel for optimum wound healing purpose. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 1567–1580. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S198413
Diretrizes da prática de eutanásia do CONCEA (2013). In: Ministério Da Ciência, Tecnologia e Inovação, Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação Animal – CONCEA. https://antigo.mctic.gov.br/mctic/opencms/legislacao/outros_atos/resolucoes/Resolucao_CONCEA_n_37_de_15022018.html
National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals: Environment, housing and management. 8th ed. The National Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/12910
Percie du Sert N, Hurst V, Ahluwalia A, Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2020;18(7):e3000410. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000410
Grover HS, Kapoor S, Singh A. Effect of topical simvastatin (1,2 mg) on gingival crevicular fluid interleukin-6, interleukin-8 and interleukin-10 levels in chronic periodontitis- a clinic biochemical study. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2016;6(2):85-92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobcr.2015.11.003
Abegão KGB, Bracale BN, Delfim IG, Santos ESD, Laposy CB, Nai GA, et al. Effects of heterologous platelet-rich plasma gel on standardized dermal wound healing in rabbits. Acta Cir Bras. 2015;30:209-215. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-865020150030000008
Taniguchi BA, Breda MRS, Nogueira RMB, Nai GA, Laposy CB. Fractal features of rabbit dermal wounds treated with platelet-rich plasma and topical rosuvastatin. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018;11(11):5241. (https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6963036/)
Tetila AF, Breda MRS, Nogueira RMB, Nai GA, Laposy CB. The use of platelet-rich plasma and rosuvastatin in wound healing in rabbits: a longitudinal study. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2019;32(9):1-5. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ASW.0000577136.88748.68
Azevedo, M.C.M.P.S. Aplicação do PRF em medicina dentária. 2014. 29f. 51. Dissertação (Mestrado Integrado em Medicina Dentária) – Faculdade de Medicina Dentária, Universidade do Porto – Portugal. 2014. (https://hdl.handle.net/10216/75440)
Kanashiro GP, Cassu RN. Anestesia em animais selvagens e de laboratório. In: Andrade SF. Manual de terapêutica veterinária. 3rd ed. Roca; 2008. pp.728-745.
Vendramin FS, Franco D, Schamall RF, Franco TR. Utilização do plasma rico em plaquetas autólogo em enxertos cutâneos em coelho. Rev Bras Cir Plástica. 2010;25:4-10. (https://www.rbcp.org.br/details/549/pt-BR)
Carvalho V, Gomes FSL, Carmo DJ, Batista JA, Viana MN. Planimetria como método para mensuração de feridas. Rev Mineira Enferm. 2006;10(4):425-428. https://doi.org/10.35699/reme.v10i4.50743
Sun Y, Cao Y, Zhao R, Xu F, Wu D, Wang Y. The role of autologous APRP on deep partial-thickness burn wound healing in bama pigs. J Burn Care Res. 2020;41(3):657-662. https://doi.org/10.1093/jbcr/iraa012
Xu P, Wu Y, Zhou L, Yang Z, Zhang X, Hu X, et al. Platelet-rich plasma accelerates skin wound healing by promoting re-epithelialization. Burns Trauma. 2020;8: tkaa028. https://doi.org/10.1093/burnst/tkaa028.
Kobayashi E, et al. Comparative release of growth factors from PRP, PRF, and advanced-PRF. Clin Oral Investig. 2016;20:2353-60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-016-1719-1
Khalifa OA, Elkasapy A, Sallam EA, Marei YM, Mohammed LS. Effect of Autologous platelet-rich plasma versus platelet-rich fibrin on the Second Intension Wound Healing in Dogs through higher regeneration capacity and modulation of inflammatory cytokines. Benha Vet Med J. 2021;41(1):1-7. https://doi.org/10.21608/BVMJ.2021.92616.1465
Snowden JM. Wound closure: an analysis of the relative contributions of contraction and epithelialization. J Surg Res. 1984;37(6):453-463. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4804(84)90213-0
Bull RH, Staines KL, Collarte AJ, Bain DS, Ivins NM, Harding KG. Measuring progress to healing: A challenge and an opportunity. Int Wound J. 2022;19(4):734-740. https://doi.org/0.1111/iwj.13669
Balse NS, Baliga S. “Evaluation of wound healing and bone regeneration using autologous platelet-rich plasma and platelet-rich fibrin postextractions”: A comparative study. Indian J Health Sci Biomed Res KLEU. 2017;10(2):167-172. https://doi.org/10.4103/kleuhsj.ijhs_395_16
Yerke LM, Jamjoom A, Zahid TM, Cohen RE. The effect of platelet-rich fibrin, calcium sulfate hemihydrate, platelet-rich plasma and resorbable collagen on soft tissue closure of extraction sites. J Funct Biomater. 2017;8(2):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb8020017
Khalaf FH, Salih SI. Clinical and histopathological evaluation of using platelet-rich plasma and platelet-rich fibrin matrix in treatment of induced chronic open wounds in bucks. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2018;11(5):337-341. https://doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2018.v11i5.24105
Kim TH, Kim SH, Sándor GK, Kim YD. Comparison of platelet-rich plasma (APRP), platelet-rich fibrin (APRF), and concentrated growth factor (CGF) in rabbit-skull defect healing. Arch Oral Biol. 2014;59(5):550-558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2014.02.004
Bansal S, Garg A, Khurana R, Chhabra P. Platelet-rich fibrin or platelet-rich plasma–which one is better? an opinion. Indian J Dent Sci. 2017;9(Suppl 1):S49-S52. https://doi.org/10.4103/IJDS.IJDS_55_17
Xiong S, Qiu L, Su Y, Zheng H, Yi C. Platelet-rich plasma and platelet-rich fibrin enhance the outcomes of fat grafting: a comparative study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;143(6):1201e-1212e. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000005676
Pradeep AR, Karvekar S, Nagpal K, Patnaik K, Raju A, Singh P. Rosuvastatin 1.2 mg in situ gel combined with 1: 1 mixture of autologous platelet‐rich fibrin and porous hydroxyapatite bone graft in surgical treatment of mandibular class II furcation defects: A randomized clinical control trial. J Periodontol. 2016;87(1):5-13. https://doi.org/10.1902/jop.2015.150131
Gautam K, Kapoor A, Mathur S, Ali AR, Choudhary A, Shekhawat A. Comparative evaluation of autogenous bone graft and autologous platelet-rich fibrin with and without 1.2 mg in situ rosuvastatin gel in the surgical treatment of intrabony defect in chronic periodontitis patients. Contemp Clin Dent. 2022;13(1):69. https://doi.org/10.4103/ccd.ccd_740_20
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Brazilian Animal Science/ Ciência Animal Brasileira

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g. in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).
Data statement
-
The research data is available on demand, condition justified in the manuscript































