Achados patológicos e incidentais em anuros do Ceará, nordeste brasileiro
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1590/1809-6891v25e-77787EResumo
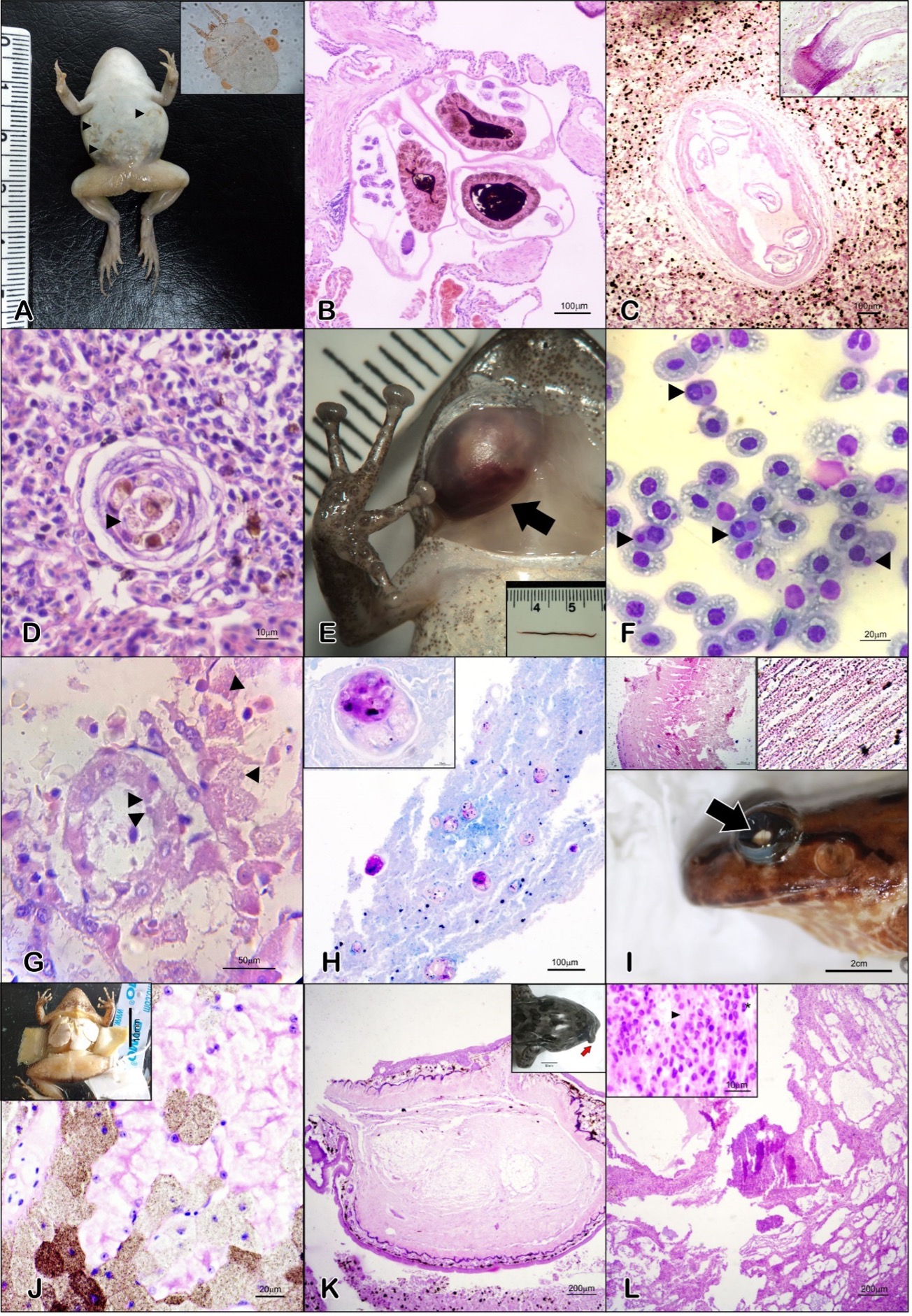
Anfíbios são um dos grupos de vertebrados mais ameaçados globalmente, e os anuros são sua ordem mais representativa. Doenças infecciosas emergentes têm sido associadas ao declínio global das espécies de anfíbios, fenômeno relatado em todo o mundo. Na região Nordeste, o Ceará tem uma abundante anurofauna, com cerca de 5% de suas espécies sendo consideradas criticamente ameaçadas. Em projetos de pesquisa, várias patologias são observadas em anuros silvestres locais, contudo, poucos casos têm sido publicados. O objetivo deste trabalho foi reunir achados patológicos e incidentais em anuros nativos do estado do Ceará, nordeste do Brasil. Os achados foram registrados durante necrópsias e exames clínicos. A amostra incluiu 38 espécimes, distribuídos em 13 espécies, originários de 13 localidades, examinados entre 2010 e 2022. A maioria das lesões (71%, n = 38) apontou para fisiopatologia inflamatória, incluindo infecções parasitárias com agentes lesionais - lesões granulomatosas e necrotizantes com inclusões intracitoplasmáticas, compatíveis com Mycobacteria e Ranavírus, respectivamente. Fibrolipoma e carcinoma hepatocelular se apresentaram como nódulos únicos, estando o último associado a uma infecção helmíntica cística. Calcinose hepática difusa representou doença de etiologia tóxico/metabólica. Catarata bilateral foi a alteração ocular mais frequente (60%, n=5), mas sem diagnóstico etiológico conclusivo. Indícios de doenças infecciosas foram detectados e necessitam de técnicas complementares de diagnóstico etiológico. A falta de laboratórios locais ou parceiros com técnicas diagnósticas específicas limitou alguns diagnósticos definitivos. Os achados aqui apresentados colocam o estado do Ceará no mapa de doenças preocupantes da anurofauna, que necessitam ser monitoradas.
Downloads
Referências
Frost D. Amphibian species of the world [Internet]. Amphibian Species of the World 6.1, an Online Reference. [cited 2023 Mar 12]. Available from: https://amphibiansoftheworld.amnh.org/
Wells KD. The Ecology & Behavior of Amphibians. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press; 2007.
Duellman WE, Trueb L. Biology of Amphibians. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1986.
Nunes-de-Almeida CHL, Haddad CFB, Toledo LF. A revised classification of the amphibian reproductive modes. Salamandra. 2021;57(3):413-427. Available from: https://www.salamandra-journal.com/index.php/contents/2021-vol-57/2054-nunes-de-almeida-c-h-l-c-f-b-haddad-l-f-toledo-1/file
Thibaudeau G, Altig R. Endotrophic Anurans. In: McDiarmic R, Altig R, editors. Tadpoles: the biology of anuran larvae. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press; 1999. p. 170-80.
Harfoot MBJ, Johnston A, Balmford A, Burgess ND, Butchart SHM, Dias MP, et al. Using the IUCN Red List to map threats to terrestrial vertebrates at global scale. Nature Ecology & Evolution. 2021;5:1510-1519. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-021-01542-9
Daszak P, Berger L, Cunningham AA, Hyatt AD, Green DE, Speare R. Emerging Infectious Diseases and Amphibian Population Declines. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 1999;5(6):735-748. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3201/eid0506.990601
Densmore CL, Green DE. Diseases of amphibians. ILAR Journal. 2007;48(3):235-54. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar.48.3.235
Scheele BC, Pasmans F, Skerratt LF, Berger L, Martel A, Beukema W, et al. Amphibian fungal panzootic causes catastrophic and ongoing loss of biodiversity. Science. 2019;363(6434):1459-1463. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aav0379
Carvalho T, Becker CG, Toledo LF. Historical amphibian declines and extinctions in Brazil linked to chytridiomycosis. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 2017;284(1848):20162254. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2016.2254
Toledo LF, Britto FB, Araújo O, Giasson L, Haddad C. The occurrence of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in Brazil and the inclusion of 17 new cases of infection. South American Journal of Herpetology. 2006;1(3):185-91. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2994/1808-9798(2006)1[185:TOOBDI]2.0.CO;2
Ruggeri J, Ribeiro LP, Pontes MR, Toffolo C, Candido M, Carriero MM, et al. Discovery of Wild Amphibians Infected with Ranavirus in Brazil. Journal of Wildlife Diseases. 2019;55(4):897-902. Available from: https://doi.org/10.7589/2018-09-224
Herczeg D, Ujszegi J, Kásler A, Holly D, Hettyey A. Host–multiparasite interactions in amphibians: a review. Parasites & Vectors. 2021;14(1):296. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-021-04796-1
Pessier AP. Amphibia. In: McAloose D, Leger JS, Terio KA, editors. Pathology of wildlife and zoo animals. London: Academic Press an imprint of Elsevier; 2018. p.919-950.
Darzins E. The epizootic of tuberculosis among the Gias in Bahia. Acta Tuberculosea Scandinavica. 1952;26(1-2):170-174. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14952353/
Bartralot R, Pujol RM, García-Patos V, Sitjas D, Martín-Casabona N, Coll P, et al. Cutaneous infections due to nontuberculous mycobacteria: histopathological review of 28 cases. Comparative study between lesions observed in immunosuppressed patients and normal hosts. Journal of Cutaneous Pathology. 2000;27(3):124-129. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0560.2000.027003124.x
Cassiano-Lima D, Ávila RW, Castro DP, Roberto IJ, Borges-Nojosa DM. Lista de anfíbios do Ceará [Internet]. SEMA-CE. 2021 [cited 2023 Mar 10]. Available from: https://www.sema.ce.gov.br/fauna-do-ceara/vertebrados/anfibios/
Roberto IJ, Loebmann D. Composition, distribution patterns, and conservation priority areas for the herpetofauna of the state of Ceará, northeastern Brazil. Salamandra. 2016;52(2):134-152. Available from: https://www.salamandra-journal.com/index.php/contents/2016-vol-52/569-roberto-i-j-d-loebmann/file
Brasil. Ministério do Meio Ambiente. Gabinete do Ministro. Portaria no 148. Atualização da Lista Nacional de Espécies Ameaçadas de Extinção Brasília, DF; 2022. Portuguese. Available from: https://www.icmbio.gov.br/cepsul/images/stories/legislacao/Portaria/2020/P_mma_148_2022_altera_anexos_P_mma_443_444_445_2014_atualiza_especies_ameacadas_extincao.pdf
Preuss JF, Lambertini C, Leite D da S, Toledo LF, Lucas EM. Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in near threatened and endangered amphibians in the southern Brazilian Atlantic Forest. North Western Journal of Zoology. 2015;11(2):360-362. Available from: https://biozoojournals.ro/nwjz/content/v11n2/nwjz_142504_Preuss.pdf
Benício RA, Carvalho T, Barbosa MD, Costa J de, da Silva FC, Fonseca MG. Worrying news for Brazilian Caatinga: Prevalence of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in Amphibians. Tropical Conservation Science. 2019;12:194008291989262. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/1940082919892626
Carnaval AC, Puschendorf R, Peixoto OL, Verdade VK, Rodrigues MT. Amphibian Chytrid fungus broadly distributed in the Brazilian Atlantic Rain Forest. EcoHealth. 2006;3(1):41-48. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10393-005-0008-2
Morais D, Rodrigues M, Ávila R, da Silva R. Visceral mycobacteriosis in amphibians from the Brazilian Caatinga region. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms. 2021;145(34):139-144. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3354/dao03604
Bassini-Silva R, Huang-Bastos M, Morais DH, Alcantara EP, Ávila RW, Welbourn C, et al. A new species of Hannemania oudemans, 1911 (Trombidiformes: Leeuwenhoekiidae) from Brazil. Journal of Natural History. 2021;55(19-20):1277-1287. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2021.1944687
Lins AGS, Aguiar A, Morais DH, Firmino da Silva LA, Ávila RW, Silva RJ. Helminth fauna of Leptodactylus syphax (Anura: Leptodactylidae) from Caatinga biome, northeastern Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Parasitologia Veterinária. 2017;(1):74-80. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-29612017013
Mascarenhas W, Oliveira CR, Benício RA, Ávila RW, Ribeiro SC. Nematodes of Proceratophrys ararype (Anura: Odontophrynidae), an endemic frog from the Araripe Plateau, northeastern Brazil. Biota Neotropica. 2021;21(3): e20201164. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1590/1676-0611-BN-2020-1164
Oliveira CR, Ávila RW, Morais DH. Helminths Associated with Three Physalaemus Species (Anura: Leptodactylidae) from Caatinga Biome, Brazil. Acta Parasitologica. 2019;64(1):205-212. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11686-018-00022-8
Machado M, Castro MB, Gimeno EJ, Barros SS, Riet-Correa F. Enzootic calcinosis in ruminants: A review. Toxicon. 2020 Nov;187:1–9. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2020.08.009
Wagener MG, Lehmbecker A, Bühler M, Wilkens M, Punsmann T, Ganter M. Calcinosis in a roe deer fawn (Capreolus capreolus) in Northern Germany. BMC Veterinary Research. 2020;16(1):406. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-020-02615-w
Chatigny F, Kamunde C, Creighton CM, Stevens ED. Uses and doses of local anesthetics in fish, amphibians, and reptiles. Journal of the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science. 2017;56(3):244-253. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28378704
Brasil. Resolução n°1000 de 11 de Maio de 2012. [Internet]. Brasília: Conselho Federal de Medicina Veterinária, [Cited 2022 Set 18]. Portuguese. Available from: http://ts.cfmv.gov.br/manual/arquivos/resolucao/1000.pdf
Brasil. Resolução No 55, de 5 de Outubro de 2022. Diretriz Brasileira para o Cuidado e a Utilização de Animais em Atividades de Ensino ou de Pesquisa Científica. [Internet]. Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação Animal, [Cited 2022 Dec 15]. Portuguese. Available from: https://www.gov.br/mcti/pt-br/composicao/conselhos/concea/arquivos/arquivo/legislacao/resolucao-normativa-no-55-de-5-de-outubro-de-2022.pdf
Campbell TC. Exotic Animal Hematology and Cytology. 4th ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2015. 402 p.
Pessier AP, Pinkerton M. Practical gross necropsy of amphibians. Seminars in Avian and Exotic Pet Medicine. 2003;12(2):81-88. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1053/saep.2003.127884
Tadrous PJ. Diagnostic Criteria Handbook in Histopathology: a surgical pathology vade mecum. 1st ed. West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2007. 422 p.
Azulay R, Andrade L. Demonstration of Mycobacterium leprae in sections in 532 cases of leprosy: comparative study between the Ziehl-Klingmuller and the Wade-Fite techniques. International Journal of Leprosy. 1954;22(2):195-199. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/13211040/
Greenwood N, Fox H. A comparison of methods for staining tubercle bacilli in histological sections. Journal of Clinical Pathology. 1973;26(4):253-257. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.26.4.253
R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing; 2022. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Available from: https://www.R-project.org/.
Roberto IJ, Loebmann D. Composition, distribution patterns, and conservation priority areas for the herpetofauna of the state of Ceará, northeastern Brazil. Salamandra. 2016;52(2):134-152. Available from: https://www.salamandra-journal.com/index.php/contents/2016-vol-52/569-roberto-i-j-d-loebmann/file
Borges-Leite MJ, Mota-Rodrigues JF, Borges-Nojosa DM. Herpetofauna of a coastal region of northeastern Brazil. Herpetology Notes. 2014;7:405-413. Available from: https://www.seh-herpetology.org/journals/herpetology-notes/back-issues/volume-7-2014
Castro DP, Mângia S, Magalhães F de M, Röhr DL, Camurugi F, Silveira-Filho RR da, et al. Herpetofauna of protected areas in the Caatinga VI: the Ubajara National Park, Ceará, Brazil. Herpetology Notes. 2019;12:727-742. Available from: https://www.biotaxa.org/hn/article/view/31446
Castro DP, Mota-Rodrigues JF, Cassiano-Lima D, Borges-Nojosa DM. Composition and diversity of anurans from rock outcrops in the Caatinga Biome, Brazil. Herpetology Notes. 2018;11:189-195. Available from: https://www.biotaxa.org/hn/article/view/23510
Ribeiro SC, Roberto IJ, Sales DL, Ávila RW, Almeida WO. Amphibians and reptiles from the Araripe bioregion, northeastern Brazil. Salamandra. 2012;48(3):133-146. Available from: https://www.salamandra-journal.com/index.php/contents/2012-vol-48/292-ribeiro-s-c-i-j-roberto-d-l-sales-r-w-avila-w-o-almeida/file
Magalhães FM, Lyra ML, Carvalho TR, Baldo D, Brusquetti F, Burella P, et al. Taxonomic Review of South American Butter Frogs: Phylogeny, Geographic Patterns, and Species Delimitation in the Leptodactylus latrans Species Group (Anura: Leptodactylidae). Herpetological Monographs. 2020;34(1):131-177. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1655/HERPMONOGRAPHS-D-19-00012
Chaves MF, Moura GJB, Baptista JS, Dantas AP, Teixeira VW, Teixeira ÁAC. Environmental and abiotic factors interfere in Leptodactylus macrosternum (Anura, Leptodactylidae) reproduction despite no changes in sexual hormones levels. Research, Society and Development. 2021;10(8):e46110817627. Available from: https://doi.org/10.33448/rsd-v10i8.17627
Braga RR, Gondim PM, Matushima ER. Histopathology of Endocrine Organs of Miranda’s White-Lipped Frogs (Leptodactylus macrosternum) from Cultivated and Non-Cultivated Regions in Semi-Arid Northeastern Brazil. Journal of Comparative Pathology. 2022;192:1-10. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcpa.2021.12.002
Braga RR, Gondim PM, Pereira RM, Batista BL, Matushima ER. Leptodactylus macrosternum (Anura: Leptodactylidae) as a bioindicator of potentially toxic chemical elements in irrigated perimeters in northeastern Brazil. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology. 2022;4:124-131. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enceco.2022.02.003
Alvarado-Rybak M, Valenzuela-Sánchez A, Cevidanes A, Peñafiel-Ricaurte A, Uribe-Rivera DE, Flores E, et al. High prevalence of chigger mite infection in a forest-specialist frog with evidence of parasite-related granulomatous myositis. Parasitology Research. 2018;117(5):1643-1646. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-018-5822-x
Aisien MSO, Uwagbae M, Edo-Taiwo O, Imasuen AA, Ovwah E. Pattern of parasitic infections in anurans from a mangrove community of the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Zool. 2015;13(December):50–5. Available from: https://www.ajol.info/index.php/tzool/article/view/142143/131882#:~:text=oxyrynchus.,%25%20and%20nematodes%2C%2028.96%25.
Umberger CM, de Buron I, Roumillat WA, McElroy EJ. Effects of a muscle‐infecting parasitic nematode on the locomotor performance of their fish host. J Fish Biol. 2013 Apr 13;82(4):1250–8. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.12061
Kölle P, Hoffman R. Incidence of nephropathies in European Tortoises. Proceedings of the Association of Reptiles and Amphibians Veterinarians. 2002;33-35.
Galindo GM, Rodrigues RA, Marcondes SF, Soares P, Tavares LER, Fernandes CE. Morphological and morphometric features of nematode-cysts in Gymnotus inaequilabiatus liver in the Brazilian Pantanal. Revista Brasileira de Parasitologia Veterinária. 2017;26(3):285-291. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-29612017044
Melo FTV, Melo CSB, Nascimento LCS, Giese EG, Furtado AP, Santos JN. Morphological characterization of Eustrongylides sp. larvae (Nematoda, Dioctophymatoidea) parasite of Rhinella marina (Amphibia: Bufonidae) from Eastern Amazonia. Revista Brasileira de Parasitologia Veterinária. 2016;25(2):235-239. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-29612016024
Jones HI. Pathology associated with Physalopterid larvae (Nematoda: Spiruridae) in the gastric tissues of Australian reptiles. Journal of Wildlife Diseases. 1995;31(3):299-306. Available from: https://doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-31.3.299
Juan-Sallés C, Almagro V, Carbonell L, Valls X, Montesinos A, Fernández-Bellon H. Enfermedades infecciosas y parasitarias en anfibios en cautividad: estudio retrospectivo de 131 pacientes. Clínica Veterinaria de Pequeños Animales. 2020;40(1):15-27. Available from: https://www.clinvetpeqanim.com/img/pdf/2025110247.pdf
Goater CP, Semlitsch RD, Bernasconi MV. Effects of Body Size and Parasite Infection on the Locomotory Performance of Juvenile Toads, Bufo bufo. Oikos. 1993;66(1):129-136. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2307/3545205
Wetsch O, Strasburg M, McQuigg J, Boone MD. Is overwintering mortality driving enigmatic declines? Evaluating the impacts of trematodes and the amphibian chytrid fungus on an anuran from hatching through overwintering. PLOS ONE. 2022;17(1):e0262561. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0262561
Sanil NK, Asokan PK, John L, Vijayan KK. Pathological manifestations of the acanthocephalan parasite, Tenuiproboscis sp. in the mangrove red snapper (Lutjanus argentimaculatus) (Forsskål, 1775), a candidate species for aquaculture from Southern India. Aquaculture. 2011;310(3-4):259-266. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2010.10.027
Choi C-J, Lee H-J, Go J-H, Park Y-K, Chai J-Y, Seo M. Extraintestinal Migration of Centrorhynchus sp. (Acanthocephala: Centrorrhynchidae) in Experimentally Infected Rats. The Korean Journal of Parasitology. 2010;48(2):139-143. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2010.48.2.139
Stutz WE, Blaustein AR, Briggs CJ, Hoverman JT, Rohr JR, Johnson PTJ. Using multi‐response models to investigate pathogen coinfections across scales: Insights from emerging diseases of amphibians. Methods in Ecology and Evolution. 2017;9(4):1109-1120. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12938
Campião KM, Ribas AC de A, Morais DH, Silva RJ da, Tavares LER. How Many Parasites Species a Frog Might Have? Determinants of Parasite Diversity in South American Anurans. PLOS ONE. 2015;10(10):e0140577. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0140577
Szuroczki D, Richardson JML. The role of trematode parasites in larval anuran communities: an aquatic ecologist’s guide to the major players. Oecologia. 2009;161(2):371-385. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-009-1388-8
Miller D, Gray M, Storfer A. Ecopathology of Ranaviruses Infecting Amphibians. Viruses. 2011 Nov 22;3(11):2351–73.
World Organisation for Animal Health. Infection with Ranavirus [Internet]. Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals. 2022 [cited 2022 Nov 1]. Available from: https://www.woah.org/en/disease/ranavirosis/
Miller DL, Pessier AP, Hick P, Whittington RJ. Comparative Pathology of Ranaviruses and Diagnostic Techniques. In: Gray MJ, Chinchar VG, editors. Ranaviruses lethal pathogens of ectothermic vertebrates. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2015. p. 171-208.
Jancovich JK, Qin Q, Zhang Q, Chinchar VG. Ranavirus Replication: Molecular, Cellular, and Immunological Events. In: Gray MJ, Chinchar VG, editors. Ranaviruses lethal pathogens of ectothermic vertebrates. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2015. p. 105-140.
Braga RR, Eleutério BKN, Lima RCS, Quirino TF. Marked systemic necrotizing disease in a Leptodactylus vastus (Anura: Leptodactylidae) from an urban reserve in northeastern Brazil. Brazilian Journal of Veterinary Pathology, 2023;16(3):203-207. Available from: DOI: https://10.24070/bjvp.1983-0246.v16i3p203-207
Fremont-Rahl JJ, Ek C, Williamson HR, Small PLC, Fox JG, Muthupalani S. Mycobacterium liflandii Outbreak in a Research Colony of Xenopus (Silurana) tropicalis Frogs. Veterinary Pathology. 2011;48(4):856-867. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1177/0300985810388520
Milnes EL, Delnatte P, Lentini A, May K, Ma J, Jamieson FB, et al. Mycobacteriosis in a Zoo Population of Chinese Gliding Frogs (Rhacophorus dennysi) Due to Mycobacterium marinum. Journal of Herpetological Medicine and Surgery. 2020;30(1):14-20. Available from: https://doi.org/10.5818/19-03-186.2
Ackermann M. Inflammation and Healing. In: Zachary JF, editor. Pathologic basis of veterinary diseases. 7th ed. Saint Louis: Elsevier; 2022. p. 104-170.
Seiler P, Ulrichs T, Bandermann S, Pradl L, Jörg S, Krenn V, et al. Cell‐Wall Alterations as an Attribute of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Latent Infection. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 2003;188(9):1326-1331. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1086/378563
Fukunaga H, Murakami T, Gondo T, Sugi K, Ishihara T. Sensitivity of Acid-Fast Staining for Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Formalin-fixed Tissue. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2002;166(7):994-997. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.2111028
Riaz SM, Bjune GA, Wiker HG, Sviland L, Mustafa T. Mycobacterial antigens accumulation in foamy macrophages in murine pulmonary tuberculosis lesions: Association with necrosis and making of cavities. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology. 2020;91(4): e12866. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/sji.12866
Elkan E. Some interesting pathological cases in amphibians. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London. 1960;134(2):275-296. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7998.1960.tb05593.x
Griffith A. Tuberculosis in cold-blooded animals. In: A system of bacteriology. London: Medical Research Council; 1930. p. 326-332.
Küster E. Über Kaltblütertuberkulose. Munchener medizinische Wochenschrift. 1905;52:57-59 (cited by Barros et al., 1988).
Lichtenstein S. Ein Fall von spontaner Froschtuberkulose. Centralblatt für Bakteriologie, Parasitenkunde. 1920;85:249-252 (cited by Barros et al., 1988).
Barros G, Langenegger C, Langenegger J, Peixoto P. Surto de micobacteriose em criação de rãs (Rana catesbeiana) causado por Mycobacterium marinum. Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira. 1988;8(3/4):75-80. Portuguese.
Darzins E. The epizootic of tuberculosis among the Gias in Bahia. Acta Tuberculosea Scandinavica. 1952;26(1-2):170-174. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14952353/
Ferreira R, Fonseca L de S, Afonso AM, da Silva MG, Saad MH, Lilenbaum W. A report of mycobacteriosis caused by Mycobacterium marinum in bullfrogs (Rana catesbeiana). The Veterinary Journal. 2006;171(1):177-180. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tvjl.2004.08.018
Bartralot R, Pujol RM, García-Patos V, Sitjas D, Martín-Casabona N, Coll P, et al. Cutaneous infections due to nontuberculous mycobacteria: histopathological review of 28 cases. Comparative study between lesions observed in immunosuppressed patients and normal hosts. Journal of Cutaneous Pathology. 2000;27(3):124-129. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0560.2000.027003124.x
Sánchez-Morgado JM, Gallagher A, Johnson LK. Mycobacterium gordonae infection in a colony of African clawed frogs (Xenopus tropicalis). Laboratory Animals. 2009;43(3):300-303. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1258/la.2008.008035
Dubois A. Anomalies and mutations in natural populations of the Rana esculenta complex (Amphibia, Anura). Mitteilungen aus dem Museum für Naturkunde in Berlin Zoologisches Museum und Institut für Spezielle Zoologie [Berlin]. 1979;55(1):59-87.
Martof B. Factors influencing size and composition of populations of Rana clamitans. American Midland Naturalist. 1956;56(1):224-245. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.2307/2422457
Gray HM, Ouellet M, Green DM, Rand AS. Traumatic injuries in two neotropical frogs, Dendrobates auratus and Physalaemus pustulosus. Journal of Herpetology. 2002;36(1):117-121. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1670/0022-1511(2002)036[0117:tiitnf]2.0.co;2
Orós J. Pseudogout. In: Divers SJ, Stahl SJ, editors. Mader’s reptile and Amphibian Medicine and Surgery. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2019. pp.1333-1334.
Keel MK, Ruiz AM, Fisk AT, Rumbeiha WK, Davis AK, Maerz JC. Soft-tissue mineralization of bullfrog larvae (Rana catesbeiana) at a wastewater treatment facility. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation. 2010;22:655-660. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1177/104063871002200430
Balls M. Spontaneous Neoplasms in Amphibia: A Review and Descriptions of Six New Cases. Cancer Research. 1962;22(10):1142-1154. Available from: https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/22/10/1142/474833/Spontaneous-Neoplasms-in-Amphibia-A-Review-and
Hopewell E, Harrison SH, Posey R, Duke EG, Troan B, Harrison T. Analysis of Published Amphibian Neoplasia Case Reports. Journal of Herpetological Medicine and Surgery. 2020;30(3):148-155. Available from: https://doi.org/10.5818/19-09-212.1
Khudolei V, Ermoshchenkov V. Carcinogenic action of diethylstilbestrol on frogs. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 1976;81:898-900. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00803017
Abdel-Rahim AY. Parasitic Infections and Hepatic Neoplasia. Digestive Diseases. 2001;19(4):288-291. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1159/000050695
Maruszewska-Cheruiyot M, Stear MJ, Machcińska M, Donskow-Łysoniewska K. Importance of TGFβ in Cancer and Nematode Infection and Their Interaction—Opinion. Biomolecules. 2022;12(11):1572. Available from: https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111572
Aroch I, Ofri R, Sutton GA. Ocular Manifestations of Systemic Diseases. Slatter’s Fundamentals of Veterinary Ophthalmology. 2008;374-418. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-072160561-6.50021-6
Burton EC, Miller DL, Styer EL, Gray MJ. Amphibian ocular malformation associated with frog virus 3. The Veterinary Journal. 2008;177(3):442-444. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.05.006
Brooks DE, Jacobson ER, Wolf ED, Clubb S, Gaskin JM. Panophthalmitis and otitis interna in fire-bellied toads. Journal of American Veterinary Medical Association. 1983;183(11):1198-201. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6643232/
Olson ME, Gard S, Brown M, Hampton R, Morck DW. Flavobacterium indologenes infection in leopard frogs. Journal of American Veterinary Medical Association. 1992;201(11):1766-1770. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1293124/
Weiter JJ, Roh S. Viral infections of the choroid and Retina. Infectious Disease Clinics of North America. 1992;6(4):875-891. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1460268/
Forzán MJ, Jones KM, Ariel E, Whittington RJ, Wood J, Markham RJ, et al. Pathogenesis of Frog Virus 3 (Ranavirus, Iridoviridae) infection in wood frogs (Rana sylvatica). Veterinary Pathology. 2017;54(3):531-548. Available from:
https://doi.org/10.1177/0300985816684929
Monini M, Ruggeri FM. Antigenic peptides of the Epizootic hematopoietic necrosis virus. Virology. 2002;297(1):8–18. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1006/viro.2002.1410
Hooks JJ, Detrick B, Nussenblatt R. Infections associated with retinal autoimmunity. Infection and Autoimmunity. 2004:691-700. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-044451271-0.50054-5
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2024 Ciência Animal Brasileira / Brazilian Animal Science

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Autores que publicam nesta revista concordam com os seguintes termos:
- Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).






























