In vitro toxicity of Niedenzuella (Tetrapterys) multiglandulosa on bovine embryos
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1590/1809-6891v23e-71762EAbstract
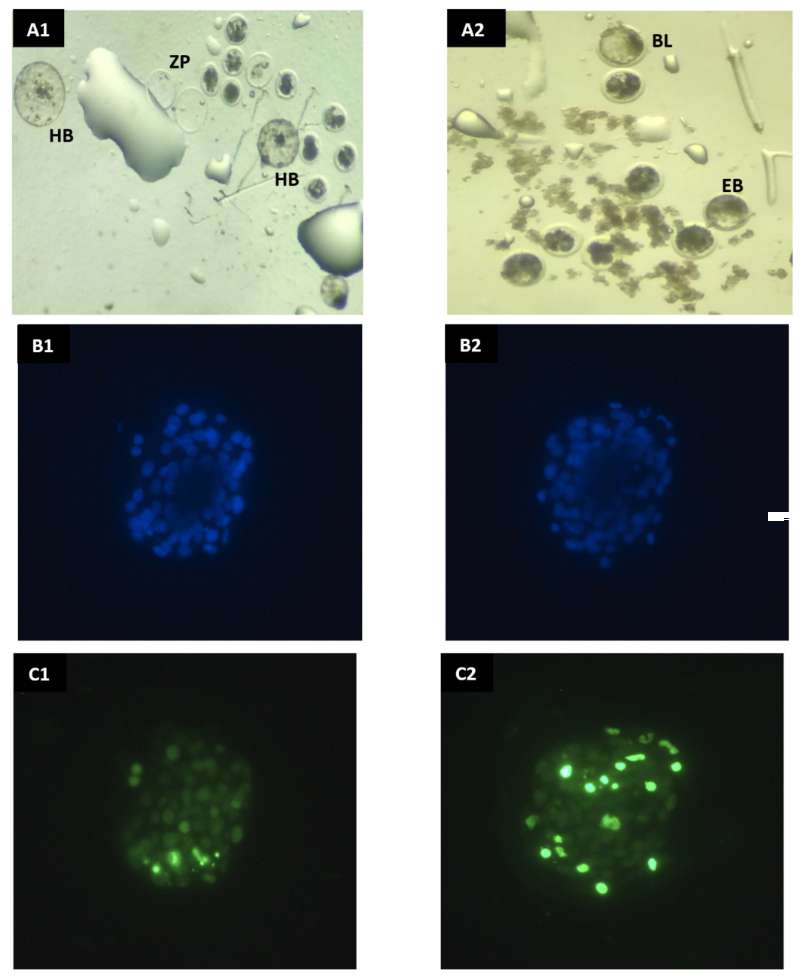
Niedenzuella (Tetrapterys) multiglandulosa, a vine plant found in Brazil, has been correlated to outbreaks of poisoning in cattle and buffaloes, generating economic losses related to the death due to heart failure, miscarriage, abortion, stillbirth, and neonatal mortality. The aim of this study was to examine the embryotoxic potential of the aqueous plant extract on in vitro bovine embryos. In vitro study was performed in five replicates of bovine embryo culture assigned in two groups: control, in vitro embryo culture medium without the aqueous plant extract; treated group, with addition of 2.7mg/mL of aqueous plant extract (10%) to the embryo culture on the sixth day of culture. Cleavage rate was evaluated at day 2 of the cell culture. Viability, hatchability and underdevelopment of blastocysts on the seventh, eighth, and ninth days (D7, D8, and D9, respectively) of culture were assessed under stereoscopic microscope. On day 7, blastocysts were submitted to TUNEL assay to determine apoptotic index. In vitro exposure of bovine embryos to of N. multiglandulosa resulted in reduced embryo development and survival, evaluated by dark cytoplasm indicating poor morphology and poor quality with marked reduction of hatchability. We observed a significant reduction of blastocyst production/number of cleaved embryos (60.6% vs 41.5%); reduction of blastocysts production/total number of matured bovine oocytes (35.1% vs 21.3%); and embryonic hatching rates (38.0% vs 10.0%). However, no effects were observed on the apoptotic rate. In conclusion, aqueous extract of N. multiglandulosa leaves reduces bovine embryo viability in vitro, suggesting possible detrimental effects on embryo development.
Key words: apoptosis; blastocyst; toxic plant.
Downloads
References
Mamede MCH, Sebastiani R, Almeida RF, Francener A, Amorim A. Malpighiaceae: lista de Espécies da Flora do Brasil [online]. Rio de Janeiro: Jardim Botânico do Rio de Janeiro; 2015, http://www.floradobrasil.jbrj.gov.br/jabot/ floradobrasil/FB155 [accessed 30 november 2017].
Tokarnia CH, Peixoto PV, Döbereiner J, Consorte IB, Gava A. Tetrapterys spp. (Malpighiaceae), a causa de mortandades em bovinos caracterizadas por alterações cardíacas. Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira. 1989;9, 23-44.
Carvalho NM, Alonso LA, Cunha NG, Ravedutti, J, Barros CSL, Lemos RAA. Intoxicação de bovinos por Tetrapterys multiglandulosa (Malpighiaceae) em Mato Grosso do Sul. Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira. 2006;6, 139-146.
Melo MM, Vasconcelos AC, Dantas GC, Serakides R, Alzamora F. Experimental intoxication of pregnants goats with Tetrapterys multiglandulosa A. Juss. (Malpighiaceae). Arquivo Brasileiro de Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia. 2001;53, 58-65.
Kirkbride CA. Etiologic agents detected in a 10-year study of bovine abortions and stillbirths. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation. 1992;4, 175-180.
Jamaluddin, AA, Case JT, Hird DW, Blanchard PC, Peauroi JR, Anderson ML. Dairy cattle abortion in California: evaluation of diagnostic laboratory data. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation, 1996;8, 210-218.
Riet-Correa G, Terra FF, Schild AL, Riet-Correa F, Barros SS. Intoxicação experimental por Tetrapterys multiglandulosa (Malpighiaceae) em ovinos. Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira. 2005;25, 91-96.
Riet-Correa G, Riet-Correa F, Schild, AL, Barros SS, Soares MP. Abortion and neonatal mortality in sheep poisoned with Tetrapterys multiglandulosa. Veterinary Pathology. 2009;46, 960-965.
Peixoto PV, Caldas SA, França TN, Peixoto TC, Tokarnia CH. Chronic Heart Failure and Abortion Caused by Tetrapterys spp. in Cattle in Brazil. In: RIET-CORREA, F. et al. (Eds.). Poisoning by plants, mycotoxins, and related toxins. [s.l.] CAB International: London, 2011. p. 256–263.
Melo MM, Dantas-Barros AM. Triagem fitoquímica preliminar da Tetrapterys multiglandulosa A. Juss. (Malpighiaceae). Revista Brasileira de Toxicologia. 1999.v.12, p.55-62.
Russo HM, Nunes WDG, Da Silva BV, Ionashiro M, Caires FJ. Thermo analytical and spectroscopic characteristics of young and old leaves powder and methanolic extracts of Niedenzuella multiglandulosa. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry. 2018;132: 771-776.
Hood RD, Rousseaux CG, Blakley PM. Embryo and fetus. In: Haschek, WM, Rousseaux CG, Wallig MA. Editors. Handbook of Toxicologic Pathology, Cambridge: Academic Press; 2002.pp. 895-936.
Piersma AH, Bosgra S, van Duursen MB, Hermsen SA, Jonker LR, Kroese E.D, van der Linden SC, Man H, Roelofs MJ, Schulpen SH, Schwarz M, Uibel F, van Vugt-Lussenburg BM, Westerhout J, Wolterbeek AP, van der Burg B. Evaluation of an alternative in vitro test battery for detecting reproductive toxicants. Reprod Toxicol 2013; 38:53-64.
Woudenberg AB, Gröllers-Mulderij M, Snel C, Jeurissen N, Stierum R, Wolterbeek A. The bovine oocyte in vitro maturation model: a potential tool for reproductive toxicology screening. Reproductive Toxicology. 2012; 34:251–260.
Santos RR, Eric J Schoevers EJ, Roelen BAJ. Usefulness of bovine and porcine IVM/IVF models for reproductive toxicology Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology. 2014; 12:117-128.
Lorenzetti S, Altieri I, Arabi S, Balduzzi D, Bechi N, Cordelli E, Galli C, Letta F, Modina SC, Narciso L, Pacchierotti F, Villani P, Galli A, Lazzari G, Luciano AM, Paulesu L, Spano M, Mantovani A. Innovative non-animal testing strategies for reproductive toxicology: the contribution of Italian partners within the EU project ReProTect. Annali dell'Istituto Superiore di Sanita. 2011; 47:429–444.
Bull V. Efeito da Niedenzuella multiglandulosa em coelhas gestantes e em embriões bovinos produzidos in vitro. 2018. 57f. Dissertação (Mestrado em Ciência Animal), Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais.
Borboleta LR, Labarrere CR, Ribeiro AFC, Paes Leme FO, Paes PRO, Ocarino NM, Melo MM. Perfil bioquímico sanguíneo na intoxicação experimental com extratos de Mascagnia rigida (A. Juss.) Griseb. (Malpighiaceae) em coelhos. Arquivo Brasileiro de Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia. 2011;63:1113-1123.
Pedroza H P, Ferreira, MG, Melo KDA, Carvalho JG, Keller KM, Melo MM, Soto-Blanco B. Concentrações de oleandrina nas folhas de Nerium oleander de diferentes cores da floração. Ciência Rural. 2015; 45:864-866
Botelho AFM, Santos-Miranda A, Joca HC, Mattoso CRS, Oliveira MS, Pierezan F, Cruz JS, Soto-Blanco B, Melo MM. Hidroalcoholic extract from Nerium oleander L. (Apocynaceae) elicits arrhythmogenic activity. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2017;12:170-177.
Leite AC, Andrade VB, Silva EBM, Borges AM. Efeito da adição do ácido linoleico conjugado no cultivo in vitro de embriões F1 Holandês x Zebu na sobrevivência pós-vitrificação. Arquivo Brasileiro de Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia. 2017;69 (6): 1385-1392.
Panter KEE, Stegelmeier BL. Effects of xenobiotics and phytotoxins on reproduction in food animals. Veterinary Clinics of North America: Food Animal Practice. 2011;27: 429-446.
Langeloh, A, Leguizanón F, Dalsenter P. Potencial abortivo e infertilizante de plantas brasileiras contaminantes ocasionais de pastagens de bovinos e outros herbívoros de interesse econômico. Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira. 1992; 12:11-18.
Byrne AT, Southgate J, Brison DR, Leese HJ. Analysis of apoptosis in the preimplantation bovine embryo using TUNEL. Journal of Reproduction and Fertility. 1999; 117:97-105.
Campos PP, Vasconcelos AC, Melo MM. Apoptose no placentomo de cabras gestantes intoxicadas experimentalmente com cipó-preto – Tetrapterys multiglandulosa. Arquivo Brasileiro de Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia. 2004;56:19-24.
McConkey DJ. Biochemical determinants of apoptosis and necrosis. Toxicological Letters, 1998:99:157-168.
Allen RG, Tresini M. Oxidative stress and gene regulation. Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 2000; 28, 463-499.
Van Soom A, Ysebaert M, De Kruif A. Relationship between timing of development, morula morphology and cell allocation to the inner cell mass and trophectoderm in in vitro produced embryos. Molecular Reproduction and Development. 1997; 47: 47-56.
Stegelmeier BL, Davis TZ, Clayton MJ. Plant-induced reproductive disease, abortion, and teratology in livestock. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2020; 36(3):735-743. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2020.08.004..
Buroni F, Gardner DR, Boabaid FM, Oliveira LGS, de Nava G, López F, Riet-Correa F. Spontaneous abortion in cattle after consumption of Hesperocyparis (Cupressus) macrocarpa (Hartw.) Bartel and Cupressus arizonica (Greene) needles in Uruguay. Toxicon. 2020 Jul 15;181:53-56. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2020.04.104. Epub 2020 Apr 28. PMID: 32353569.
Campagna C, Ayotte P, Sirard MA, Arsenault G, Laforest JP, Bailey JL. Effect of an environmentally relevant metabolized organochlorine mixture on porcine cumulus-oocyte complexes. Reproductive Toxicololgy. 2007; 23:145–152.
Sirard MA. Factors affecting oocyte and embryo transcriptomes. Reproduction Domestic Animals. 2012; 47:148-155.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Brazilian Animal Science/ Ciência Animal Brasileira

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g. in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).































