Estimation of productive efficiency in ewes from the natural grasslands of Southern Brazil: A pilot approach
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1590/1809-6891v26e-81645EAbstract
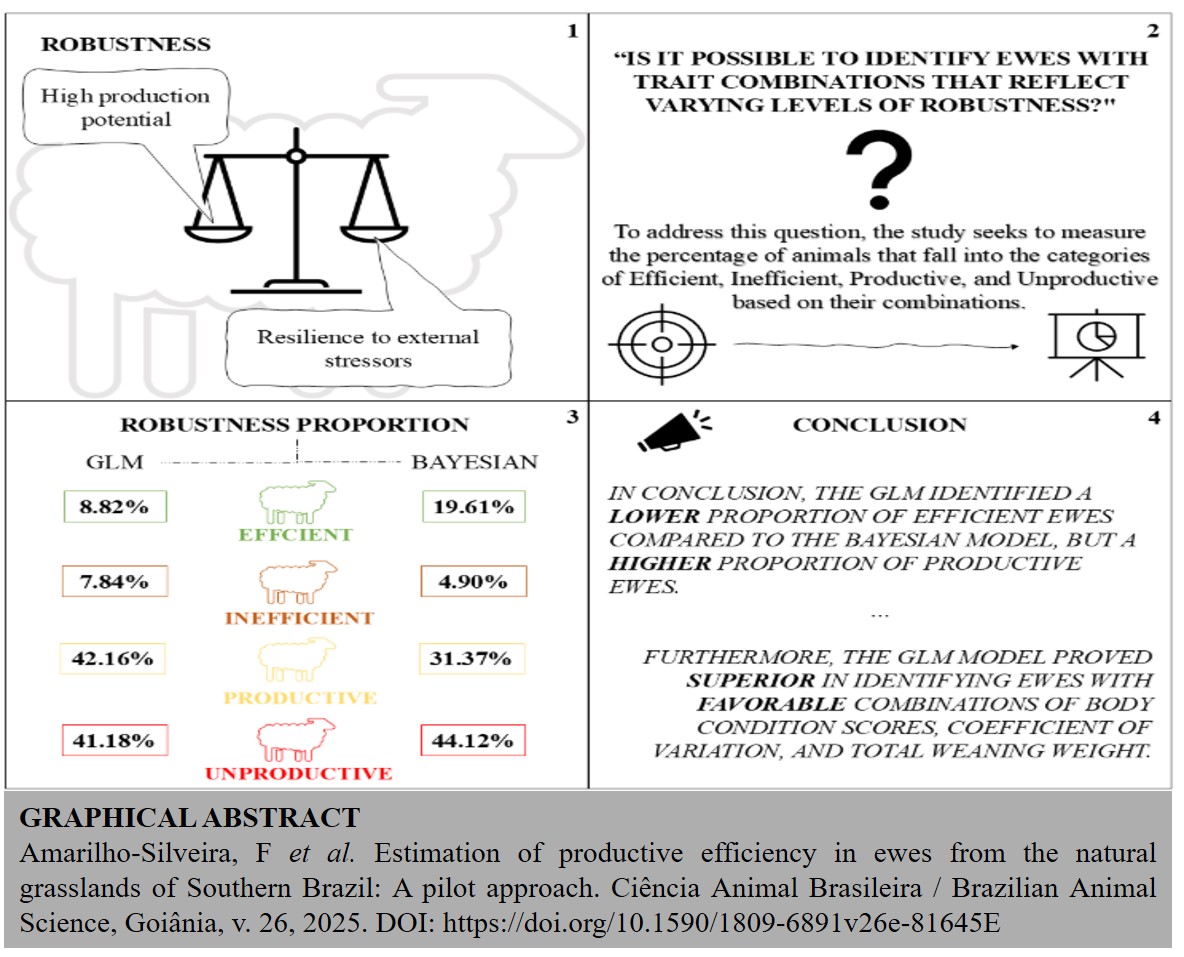
This pilot study quantified the proportion of ewes classified as Efficient, Inefficient, Productive, and Unproductive, using the data collected from an entire production cycle during 2024, provided by a sheep farm. For classification, two models were employed: a generalized linear model (GLM) using four body condition scores (BSCs) evaluations as explanatory variables, and a Bayesian mixed model (BMM) with four repeated measurements. The GLM results classified 8.82 % of ewes as Efficient, 7.84 % as Inefficient, 42.16 % as Productive, and 41.18 % as Unproductive. Conversely, the BMM categorized 19.61 % as Efficient, 4.90 % as Inefficient, 31.37 % as Productive, and 44.12 % as Unproductive. This study provides initial insights into productive efficiency indicators used in ewes, suggesting that further research over extended periods, preferably with the same animals, is required for achieving more conclusive results. Nevertheless, this approach presents a replicable evaluation model applicable to diverse scales and environments. In conclusion, GLM model proved superior in identifying ewes with favorable combinations of BSCs, coefficients of variation, and total weight of lambs at weaning.
Keywords: ewe classification; body condition score; productive efficiency indicators; generalized linear model; Bayesian mixed model.
Downloads
References
De Barbieri I, Navajas E, Douhard F, Conington J, Ramos Z, Ciappesoni G. PL-8 A review of sheep resilience. Anim - Sci Proc. 2023 Mar;14(1):11–2. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anscip.2023.01.009
Knap PW. Breeding robust pigs. Austr J Exp Agric. 2005 Aug 29;45(8):763–73. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1071/EA05041
Vialoux IM. Genetic parameters of body condition score (BCS) and effects of BCS and BCS change on ewe performance (Dissertation). [Palmerston North]: Massey University; 2020. Link: http://hdl.handle.net/10179/16391
Young MJ, Thomson BC. Robustness as a breeding objective for sheep in New Zealand. In: Hermesch S, editor. Breeding focus 2014 - Improving resilience. Armidale: Animal Genetics and Breeding Unit University of New England; 2014. p. 129–40. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.13140/2.1.5007.8403
Russel A. Body condition scoring of sheep. In: Boden E, editor. Sheep and goat practice. London: Baillière Tindall Ltd.; 1991. p. 3–10.
Bürkner P-C. brms: an R package for Bayesian multilevel models using stan. J Stat Softw. 2017;80(1):1–28. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18637/jss.v080.i01
R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2021.
Wickham H. ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis [Internet]. Springer-Verlag New York. Springer-Verlag New; 2016 [cited 2024 Dec 11]. Available from: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org
Schloerke B, Cook D, Larmarange J, Briatte F, Marbach M, Thoen E, et al. GGally: extension to “ggplot2.” R package version 2.2.1. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2024.
Olsen LR. Cross-validation for model selection. Vienna: R Core Team; 2021. p. 1–100.
Macé T, González-García E, Pradel J, Parisot S, Carrière F, Douls S, et al. Genetic analysis of robustness in meat sheep through body weight and body condition score changes over time. J Anim Sci. 2018 Nov 21;96(11):4501–11. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jas/sky318
Friggens NC, Blanc F, Berry DP, Puillet L. Deciphering animal robustness. A synthesis to facilitate its use in livestock breeding and management. Animal. 2017 Dec;11(12):2237–51. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S175173111700088X
Tait IM, Kenyon PR, Garrick DJ, Lopez-Villalobos N, Pleasants AB, Hickson RE. Associations of body condition score and change in body condition score with lamb production in New Zealand Romney ewes. N Z J Anim Sci Prod. 2019;79:91–4.
Llonch P, Hoffmann G, Bodas R, Mirbach D, Verwer C, Haskell MJ. Opinion paper: measuring livestock robustness and resilience: are we on the right track?. Animal. 2020 Apr;14(4):667–9. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S17517311190033061. De Barbieri I, Navajas E, Douhard F, Conington J, Ramos Z, Ciappesoni G. PL-8 A review of sheep resilience. Anim - Sci Proc. 2023 Mar;14(1):11–2. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anscip.2023.01.009
Knap PW. Breeding robust pigs. Austr J Exp Agric. 2005 Aug 29;45(8):763–73. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1071/EA05041
Vialoux IM. Genetic parameters of body condition score (BCS) and effects of BCS and BCS change on ewe performance (Dissertation). [Palmerston North]: Massey University; 2020. Link: http://hdl.handle.net/10179/16391
Young MJ, Thomson BC. Robustness as a breeding objective for sheep in New Zealand. In: Hermesch S, editor. Breeding focus 2014 - Improving resilience. Armidale: Animal Genetics and Breeding Unit University of New England; 2014. p. 129–40. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.13140/2.1.5007.8403
Russel A. Body condition scoring of sheep. In: Boden E, editor. Sheep and goat practice. London: Baillière Tindall Ltd.; 1991. p. 3–10.
Bürkner P-C. brms: an R package for Bayesian multilevel models using stan. J Stat Softw. 2017;80(1):1–28. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18637/jss.v080.i01
R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2021.
Wickham H. ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis [Internet]. Springer-Verlag New York. Springer-Verlag New; 2016 [cited 2024 Dec 11]. Available from: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org
Schloerke B, Cook D, Larmarange J, Briatte F, Marbach M, Thoen E, et al. GGally: extension to “ggplot2.” R package version 2.2.1. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2024.
Olsen LR. Cross-validation for model selection. Vienna: R Core Team; 2021. p. 1–100.
Macé T, González-García E, Pradel J, Parisot S, Carrière F, Douls S, et al. Genetic analysis of robustness in meat sheep through body weight and body condition score changes over time. J Anim Sci. 2018 Nov 21;96(11):4501–11. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jas/sky318
Friggens NC, Blanc F, Berry DP, Puillet L. Deciphering animal robustness. A synthesis to facilitate its use in livestock breeding and management. Animal. 2017 Dec;11(12):2237–51. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S175173111700088X
Tait IM, Kenyon PR, Garrick DJ, Lopez-Villalobos N, Pleasants AB, Hickson RE. Associations of body condition score and change in body condition score with lamb production in New Zealand Romney ewes. N Z J Anim Sci Prod. 2019;79:91–4.
Llonch P, Hoffmann G, Bodas R, Mirbach D, Verwer C, Haskell MJ. Opinion paper: measuring livestock robustness and resilience: are we on the right track?. Animal. 2020 Apr;14(4):667–9. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S1751731119003306
Additional Files
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Brazilian Animal Science/ Ciência Animal Brasileira

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g. in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).
Data statement
-
The research data is available in one or more data repository(ies)































