Ex vivo evaluation of anterior lens capsule staining in horses with three concentrations of gentian violet for surgical training
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1590/1809-6891v24e-76196EAbstract
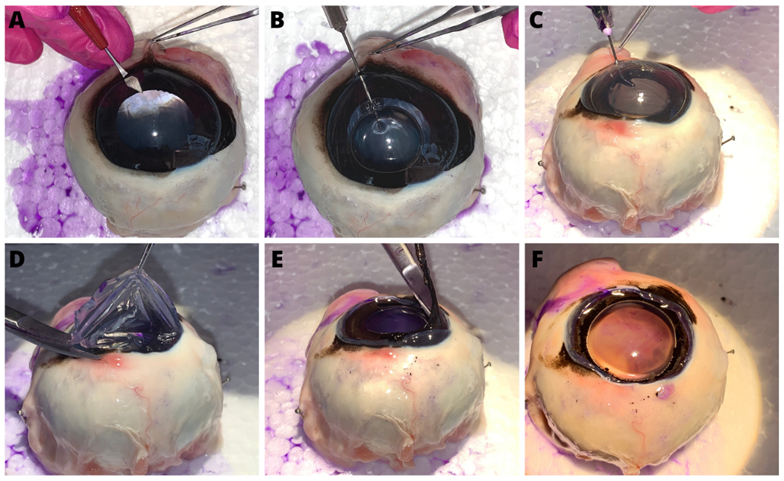
The aim of this study was to evaluate and compare the effectiveness of three concentrations of gentian violet (0.5%, 0.1% and 0.05%) for staining the anterior capsule of the lens in horses. Thirty-six post-mortem equine eyes were collected. The eyes were subdivided into three groups composed of 12 eyes each, according to the concentration of gentian violet used. The effectiveness of staining the anterior capsule of the lens with different concentrations of gentian violet was assessed using an empirical system of evaluation on adequate or inadequate staining of capsular flaps. Based on the evaluation of the examiner, the 0.1% and 0.05% concentrations of gentian violet allowed adequate visualisation of the anterior capsule for continuous curvilinear capsulotomy training, whereas the 0.5% concentration produced strong and inadequate capsular staining. The model developed using gentian violet at concentrations of 0.1% and 0.05% allowed a clear visualisation of the capsular flap, which makes it viable as a model for training the continuous curvilinear capsulotomy step in cataract surgery in horses.
Keywords: anterior capsulotomy; vital dyes; equine; wet lab; surgical training
Downloads
References
McMullen Junior RJ, Utter ME. Current developments in equine cataract surgery. Equine Veterinary Journal. Supplement. 2010;37:38-45. Available from: doi:10.1111/j.2042-3306.2010.tb05633.x.
Jhanju V, Chan E, Das S, Zhang H, Vajpayee RB. Trypan blue dye for anterior segment surgeries . Eye (Lond) 2011;25(9):1113-1120. Available from: doi:10.1038/eye.2011.139.
MCMULLEN RJ, Stoppini R. Diseases and surgery of the lens. In: Gilger BC, editor. Equine Ophthalmology. 4th ed. Hoboken : John Wiley & Sons; 2017. p.416-452. Available from: doi:10.1002/9781119782285.ch7.
Jacobs DS, Cox TA, Wagoner MD, Ariyasu RG, Karp CL. Capsule staining as an adjunct to cataract surgery. Ophthalmology. 2006;113(4):707-713. Available from: doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2006.01.024.
Hassaballa MAM, Osman AAEL. Delineating the extent of anterior capsulorhexis with gentian violet using capsulorhexis marker: a preliminary study of efficacy and toxicity in an animal model. Clinical Ophthalmology. 2011;5:831-836. Available from: doi:10.2147/OPTH.S21791.
Haeussler-Sinangin Y, Dahlhoff D, Schultz T, Dick HB. Clinical performance in continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis creation supported by a digital image guidance system. Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgery. 2017;43(3):348-352. Available from: doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2016.12.027.
Hu WF, Chen SH. Advances in capsulorhexis. Current Opinion Ophthalmology. 2019;30(1):19-24. Available from: doi: 10.1097/ICU.0000000000000539.
Sharma B, Abell RG, Arora T, Antony T, Vajpayee RB. Techniques of anterior capsulotomy in cataract surgery. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology. 2019;67(4):450-460. Available from: doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1728_18.
Eldin SAG, Mehelmy EM, Shazli EM, Mostafa YM. Experimental staining of the anterior lens capsule in albino rabbits. Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgery. 1999;25(9):1289-1294. Available from: doi: 10.1016/s0886-3350(99)00153-4.
Melles GRJ, Waard PW, Pameyer JH, Beekhuis WH. Trypan blue capsule staining I'm visualizethe capsulorhexis in cataract surgery. Journal of Cataract Refractive Surgery. 1999;25(1):7-9. Available from: doi:10.1016/s0886-3350(99)80004-2.
Rodrigues EB, Costa EF, Penha FM, Melo GB, Bottós J, Dib E, et al. The use of vital dyes in ocular surgery. Survey of Ophthalmology. 2009;54(5):576-617. Available from: doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2009.04.011.
Andjelić S, Zupančič G, Hawlina M. The effect of gentian violet on human previous lens epithelial cells. Current Eye Research. 2014;39(10):1020-1025. Available from: doi: 10.3109/02713683.2014.894077.
Simsek C, Gokmen O. The effects of vital dyes on mechanic properties of the human previous lens capsule. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology. 2020;68:66-70. Available from: doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_285_19.
Wilińska, J, Mocanu, B, Awad, D, Gousia, D, Hillner, C, Brannath, W, et al. New stains for anterior capsule surgery. Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgery. 2019;45(2): 213–218. Available from: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2018.09.016.
Dada VK, Sharma MDM, Sudan R, Sethi H, Dada T, Pangtey MS, et al. Anterior capsule staining for capsulorhexis in cases of white cataract. Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgery. 2004;30(2):326-333. Available from: doi: 10.1016/S0886-3350(03)00573-X.
Prakash G, Jhanji V, Sharma N, Gupta K, Titiyal JS, Vajpayee RB. Assessment of perceived difficulties by residents in performing routine steps in phacoemulsification surgery and in managing complications. Canadian Journal of Ophthalmology. 2009;44(3):284-287. Available from: doi: 10.3129/i09-051.
Oflaz AB, Köktekir, BE, Okudan S. Does cataract surgery simulation correlate with real- life experience? Turkish Journal of Ophthalmology. 2018;48(3):122-6. Available from: doi: 10.4274/tjo.10586.
Dong J, Yang X, Yang X, Li J. A practical continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis self-training system. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology. 2021;69(10):2678-286. Available from: doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_210_21.
Pujari A, Saluja G, Bhaskaran K, Modaboyina S, Asif MI, Agarwal T, et al. Animal and corpse human eyes for residents' surgical training in ophthalmology. Survey Ophthalmology. 2021;67(1):226-251. Available from: doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2021.05.004.
Chang YS, Tseng S, Tseng S. Comparison of dyes for cataract surgery: Part 2: Effectiveness of capsule staining in a rabbit model. Journal of Cataract and Refractive Surgery. 2005;31(4):799-804. Available from: doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2004.09.029.
Hisatomi T, Enaida H, Matsumoto H, Kagimoto T, Ueno A, Hata Y, et al. staining ability and biocompatibility of brilliant blue G. Archives of Ophthalmology. 2006;124(4):514-9. Available from: doi:10.1001/archopht.124.4.514.
Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33:159-74 . Available from: https://doi.org/10.2307/2529310
Kirkwood BR, Sterne JAC. Essential medical statistics. 2nd ed. Massachusetts: Blackwell Science; 2006. Available from: https://bcs.wiley.com/he-bcs/Books?action=index&bcsId=11848&itemId=0865428719
Pona A, Quan, EY, Cline A, Feldman SR. Review of the use of gentian violet in dermatology practice. Dermatology Online Journal. 2020;26(5):13030. Available from: https://doi.org/10.5070/D3265048772
Prabha N, Arora RD, Ganguly S, Chhabra N. Gentian violet: revisited. Indian Journal of Dermatology Venereology and Leprology. 2020;86:600-603. Available from: doi: 10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_579_19.
Ünlü K, Askünger A, Söker S, Kilinç N, Karaca C, Erdinc M. Gentian violet solution for staining the previous capsule. Indian Journal of Dermatology Venereology and Leprology. 2020;86(5):600-603. Available from: doi: 10.1016/s0886-3350(00)00360-6.
Moharana B, Singh P, Patel S, Srivastava P, Sharma B. Commentary: High fidelity and cost-effective cataract surgery training system: need of the hour. Indian Journal of Ophthalmology. 2021;69(10):2686-2687. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1877_21.
(28) Fernandez-Bueno I, Usategui-Martín R, Pastor JC, Andrés-Iglesias C. Ex-vivo method to quantifiably the staining effectiveness of anterior lens capsule dyes. Translational Vision Science & Technology. 2021;10(17):1-6. Available from: 10.1167/tvst.10.14.17.
(29) Naik MP, Sethi H, Kasiviswanathan P. Modified bandage-contact-lens used as a guide-marker for performing continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis by a first year post graduate ophthalmology resident. American Journal of Ophthalmology Case Reports. 2020; 20:100889. Available from: doi: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2020.100889.
(30) Plummer EC. Equine ophthalmology. In: Gellat K. (org.). Veterinary Ophthalmology. 6th ed. New York: Wiley-Blackwell; 2021. Available from: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Veterinary+Ophthalmology,+2+Volume+Set,+6th+Edition-p-9781119441830.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Brazilian Animal Science/ Ciência Animal Brasileira

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g. in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).































