Boas práticas na criação e manutenção de zebrafish (Danio rerio) em laboratório no Brasil
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1590/1809-6891v24e-74134EResumo
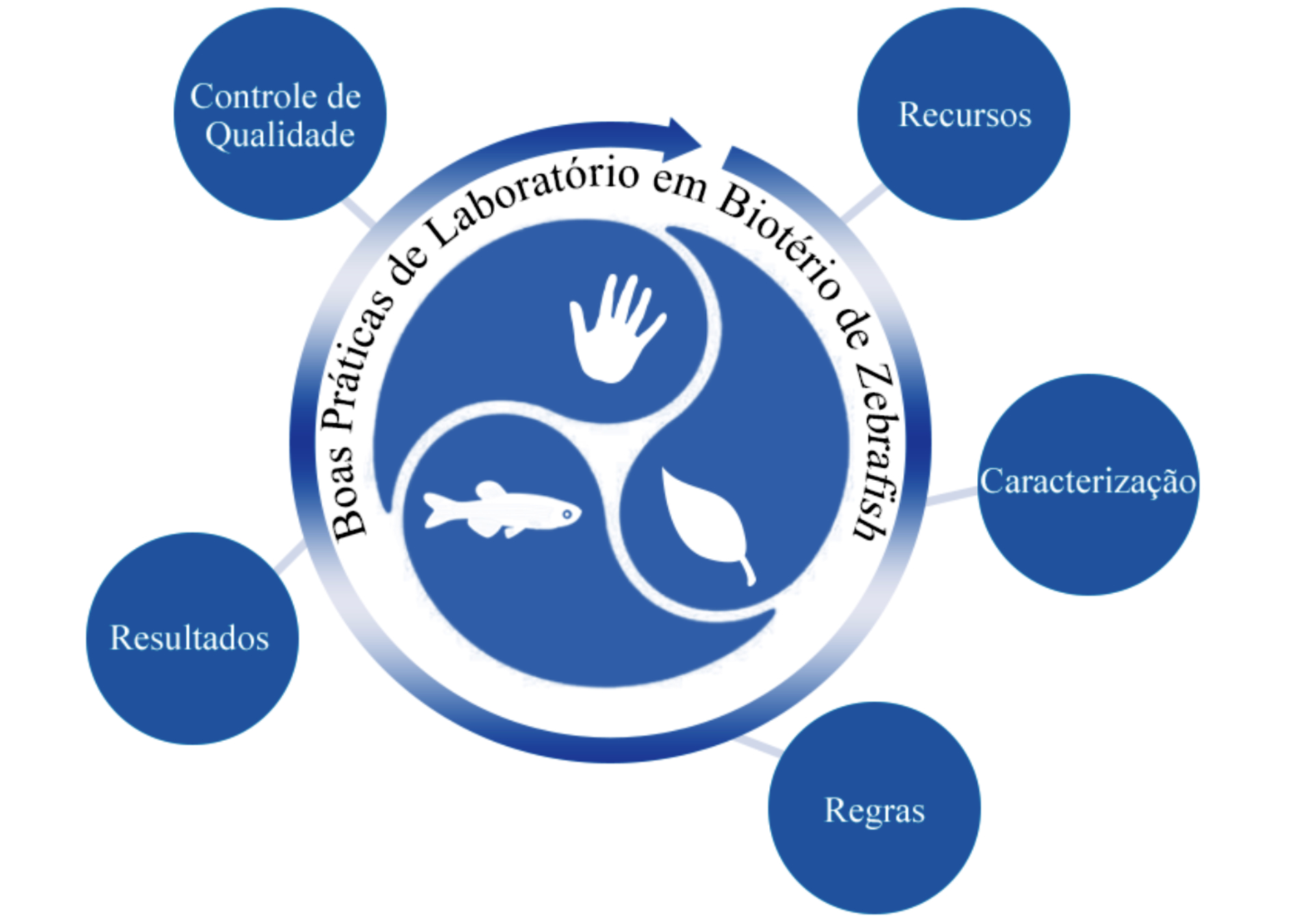
As Boas Práticas de Laboratório (BPL) são um sistema de controle de qualidade gerencial que abrange o processo organizacional e as condições sob as quais os estudos não clínicos de saúde e meio ambiente são desenvolvidos. Conforme a Organização Mundial da Saúde (OMS) as BPL devem conter cinco tópicos: recursos, caracterização, regras, resultados e controle de qualidade. O objetivo deste trabalho foi apresentar uma revisão conforme o padrão da OMS para a implementação das BPL em biotério de zebrafish. Considerando que a promoção da saúde única (animal, humana e ambiental) associada a um plano de educação, protocolos e registros são fundamentais para garantir a segurança e a integridade dos trabalhadores/pesquisadores, animais e meio ambiente assim como confiabilidade nos resultados gerados. De certa forma o Brasil ainda necessita de melhorias relacionadas ao bem-estar de organismos aquáticos (leis nacionais, acordos internacionais, programas corporativos e outros); especialmente em relação à utilização destes na pesquisa e desenvolvimento tecnológico. Desta forma, a implementação de BPL fornece uma orientação valiosa para a melhoria do bem-estar animal, e segurança do trabalhador vindo a facilitar a padronização da pesquisa.
Palavras-chave: Danio rerio; padronização; bem-estar; diretrizes reguladoras; legislação.
Downloads
Referências
Lapenta VA. Physiological assay of glucosides, toxins and poisons on gold fish, Carassius auratus. Proceedings of the Indiana Academy of Science. 1931;41:445-448.
Gersdorff WA. Relative toxicity of the cresols as demonstrated by tests with Carassius auratus. Journal of Agricultural Research. 1937;54(6):469-478.
Shlaifer A. Studies in mass physiology: effect of numbers upon the oxygen consumption and locomotor activity of Carassius auratus. Physiological Zoology. 1938;11(4):408-424. https://doi.org/10.1086/physzool.11.4.30152652.
Shaw RJ, Escobar RA, Baldwin FM. The influence of temperature and illumination on the locomotor activity of Carassius auratus. Ecology. 1938;19(2):343-346. https://doi.org/10.2307/1929654.
Ribas L, Piferrer F. The zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a model organism, with emphasis on applications for finfish aquaculture research. Reviews in Aquaculture. 2014;6(4):09-240. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12041.
Creaser WC. The Technic of Handling the Zebra Fish (Brachydanio rerio) for the Production of Eggs Which Are Favorable for Embryological Research and Are Available at Any Specified Time Throughout the Year. Copeia / JSTOR. 1934;1934(4):159-161. https://doi.org/10.2307/1435845.
Streisinger G, Walker C, Dower N, Knauber D, Singer F. Production of clones of homozygous diploid zebra fish (Brachydanio rerio). Nature. 1981;291(5813):293-296. https://doi.org/10.1038/291293a0.
Marí-Beffa M, Palmqvist P, Marín-Girón F, Montes GS, Becerra J. Morphometric study of the regeneration of individual rays in teleost tail fins. Journal of Anatomy. 1999;31(195):393-405. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-7580.1999.19530393.x.
Figueiredo MA, Ceccon CF, Almeda DV, Marins LF. Improving the production of transgenic fish germlines: in vivo evaluation of mosaicism in zebrafish (Danio rerio) using a green fluorescent protein (GFP) and growth hormone cDNA transgene co-injection strategy. Genetics and Molecular Biology. 2007;30(1):31-36. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572007000100008.
Trigueiro NSS, Canedo A, Braga DLS, Luchiari AC, Rocha TL. Zebrafish as an Emerging Model System in the Global South: Two Decades of Research in Brazil. Zebrafish. 2020;17(6):412-425. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2020.1930.
Brasil. Constituição da República Federativa do Brasil. Lei nº 11.794, de 8 de outubro de 2008. Regulamenta o inciso VII do § 1o do art. 225 da Constituição Federal, estabelecendo procedimentos para o uso científico de animais; revoga a Lei no 6.638, de 8 de maio de 1979; e dá outras providências. Diário Oficial da União; 2008; nº 196; seção 1, p.1. Portuguese.
Brasil. Presidência da República. Decreto nº 6.899, de 15 de julho de 2009. Dispõe sobre a composição do Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação Animal - CONCEA, estabelece as normas para o seu funcionamento e de sua Secretaria-Executiva, cria o Cadastro das Instituições de Uso Científico de Animais – CIUCA, mediante a regulamentação da Lei n. 11.794, de 08.10.2008, que dispõe sobre procedimentos para o uso científico de animais, e dá outras providências. Diário Oficial da União; 2009; nº 134; seção 1; p.2. Portuguese.
CONCEA, Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação Animal. Resolução Normativa CONCEA nº 34, de 27 de julho de 2017. Institui o capítulo “Peixes mantidos em instalações de instituições de ensino ou pesquisa científica para fins de estudo biológico ou biomédico I – Lambari (Astyanax), Tilápia (Tilapia, Sarotherodon e Oreochromis) e Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Diário Oficial da União. 2017; seção 1, p. 218. Portuguese.
Brand M, Granato M, Nüsslein-Volhard C. Keeping and raising zebrafish. In: Dahm R and Nüsslein-Volhard C. Zebrafish: A Practical Approach. London: IRL Press; 2002. p. 7-37.
Matthews M, Trevarrow B, Matthews J. A virtual tour of the Guide for zebrafish users. Lab Animal. 2002;31(3):34-40.
Reed B, Jennings M. Guidance on housing and care of zebrafish Danio rerio. Horsham: Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (RSPCA); 2011. 64p. (https://norecopa.no/no/textbase/guidance-on-the-housing-and-care-of-zebrafish-danio-rerio)
Canedo A, Saiki P, Santos AL, Carneiro SK, Souza, AM, Qualhato G, Brito RS, Mello-Andrade, Rocha, TL. O peixe-zebra (Danio rerio) encontra a bioética: os princípios éticos dos 10Rs na pesquisa. Ciência Animal Brasileira. 2022;23(1):e-70884. https://doi.org/10.1590/1809-6891v22e-70884.
Wolf JC, Wolfe MJ. Good laboratory practice considerations in the use of fish models. Toxicologic Pathology. 2003;31(1):53-57. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230390178739.
CONCEA, Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação Animal. Resolução Normativa CONCEA nº 32, de 06 de setembro de 2016. Baixa as Diretrizes de Integridade e de Boas Práticas para Produção, Manutenção ou Utilização de Animais em Atividades de Ensino ou Pesquisa Científica. Diário Oficial da União. 2016; seção 1, p. 5. Portuguese.
Politi FAS, Majerowicz J, Cardoso TAO, Pietro RCLR, Salgado HRN. Caracterização de biotérios, legislação e padrões de biossegurança. Revista de Ciências Farmacêuticas Básica e Aplicada. 2008;29(1)17-28. https://rcfba.fcfar.unesp.br/index.php/ojs/article/view/489.
UNDP, World Bank, WHO. Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases. Handbook: Good Laboratory Practice (GLP). World Health Organization; 2001. 225p. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/66894.
WHO, World Health Organization. Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases. Good laboratory practice training manual for the trainee: A tool for training and promoting good laboratory practice (GLP) concepts in disease endemic countries. 2nd ed. World Health Organization; 2008. 268p.
CONCEA, Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação Animal. Resolução Normativa CONCEA nº 49, de 07 de maio de 2021. Dispõe sobre a obrigatoriedade de capacitação do pessoal envolvido em atividades de ensino e pesquisa científica que utilizam animais. Diário oficial da União. 2021; seção 1, p. 5. Portuguese.
National Research Council (US). Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th ed. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2011. https://nap.nationalacademies.org/catalog/12910/guide-for-the-care-and-use-of-laboratory-animals-eighth
Kuzel MAA, Freitas TPT, Schirato GV, Souza JB, Müller CB. A importância da qualificação profissional e o trabalho em equipe no biotério de experimentação. Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Ciência em Animais de Laboratório. 2012;1(3):263-269. https://www.sbcal.org.br/old/upload/arqupload/artigo8numero3-2111e.pdf.
Trevarrow B. Zebrafish facilities for small and large laboratories. Methods in cell biology. 2004;77:565-591. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0091-679X(04)77030-2.
Lawrence C, Mason T. Zebrafish housing systems: A review of basic operating principles and considerations for design and functionality. ILAR Journal. 2012;53(2):179-191. https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar.53.2.179.
CCAC, Canadian Council on Animal Care. CCAC Guidelines: Zebrafish and other small, warm-water laboratory fish. 2020. 110p. https://ccac.ca/Documents/Standards/Guidelines/CCAC_Guidelines-Zebrafish_and_other_small_warm-water_laboratory_fish.pdf
Villamizar N, Ribas L, Piferrer F, Vera LM, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ. Impact of Daily Thermocycles on Hatching Rhythms, Larval Performance and Sex Differentiation of Zebrafish. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(12):e52153. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052153.
Spence R, Gerlach G, Lawrence C, Smith C. The behaviour and ecology of the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Biological Reviews. 2008;83(1):13-34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-185X.2007.00030.x.
Bilotta, J, Saszik S, DeLorenzo AS, Hardesty HR. Establishing and maintaining a low-cost zebrafish breeding and behavioural research facility. Behaviour Research Methods, Instruments and Computers. 1999;31(1):178-184. https://doi.org/10.3758/bf03207707.
Osterauer R, Heinz-R. Köhler. Temperature-dependent effects of the pesticides thiacloprid and diazinon on the embryonic development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquatic Toxicology. 2008;86:485-494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2007.12.013.
Barrionuevo WR, Burggren WW. O2 consumption and heart rate in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio): Influence of temperature and ambient O2. American of Journal of Physiology. 1999;276(2):R505-513. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.1999.276.2.R505.
Scott GR, Johnston IA. Temperature during embryonic development has persistent effects on thermal acclimation capacity in zebrafish. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2012;109(35):14247-14252. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1205012109.
Zhang Q, Kopp M, Babiak I, Fernandes JMO. Low incubation temperature during early development negatively affects survival and related innate immune processes in zebrafsh larvae exposed to lipopolysaccharide. Scientific Reports. 2018;8:4142. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22288-8.
Hurd MW, Debruyne J, Straume M, Cahill GM. Circadian rhythms of locomotor activity in zebrafish. Physiology & Behavior. 1998;65(3):465-472. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9384(98)00183-8.
López-Olmeda JF, Madrid JA, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ. Light and temperature cycles as zeitgebers of zebrafish (Danio rerio) circadian activity rhythms. Chronobiology International. 2006;23(3):537-550. https://doi.org/10.1080/07420520600651065.
del Pozo A, Sánchez-Férez JA, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ. Circadian rhythms of self-feeding and locomotor activity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chronobiology International. 2011;28(1):39-47. https://doi.org/10.3109/07420528.2010.530728.
Francis, M. Aquatics labs: five questions you don’t want to have to ask. Canadian Association for Laboratory Animal Science/Association Canadienne pour la Science des Animaux de Laboratoire membership magazine. 2008;42(3):25-27.
Lawrence C. The husbandry of zebrafish (Danio rerio): A review. Aquaculture. 2007;269:1-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.04.077.
Avdesh A, Chen M, Martin-Iverson MT, Mondal A, Ong D, Rainey-Smith S, Taddei K, Lardelli M., Groth DM, Verdile G, Martins RN. Regular Care and Maintenance of a Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Laboratory: An Introduction. Journal of Visualized Experiments. 2012;69:e4196. https://doi.org/10.3791/4196.
Boström ML, Berglund O. Influence of pH-dependent aquatic toxicity of ionizable pharmaceuticals on risk assessments over environmental pH ranges. Water Research. 2015; 72:154-161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.08.040.
Magalhães DP, Marques MRC, Baptista DF, Buss DF. Metal bioavailability and toxicity in freshwaters. Environmental Chemistry Letters. 2015;13:69-87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-015-0491-9.
Martinelle K, Häggström L. Mechanisms of ammonia and ammonium ion toxicity in animal cells: Transport across cell membranes, Journal of Biotechnology. 1993;30(3):339-350. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1656(93)90148-G
Wurts WA. Alkalinity and hardness in production ponds. World Aquaculture. 2002; 33:16-17.
Timmons MB, Ebeling JM, Wheaton JM, Summerelt ST, Vinci BJ. Recirculating Aquaculture Systems. 2nd ed. Ithaca (NY): Cayuga Aqua Ventures; 2002. 757p.
Aleström P, D’Angelo L, Midtlyng PJ, Schorderet DF, Schulte-Merker S, Sohm F, Warner S. Zebrafish: Housing and Husbandry Recommendations. Laboratory Animals. 2020;54(3):213-24. https://doi.org/10.1177/0023677219869037.
Kalichak F, Barcellos HHA, Idalencio R, Koakoski G, Soares SM, Pompermaier A, Rossini M, Barcellos LJG. Persistent and transgenerational effects of risperidone in zebrafish. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2019;26:26293-26303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05890-9.
Tamagno WA, Sofiatti, JRO, Alves C, Sutorillo NT, Vanin AP, Bilibio D, Pompermaier A, Barcellos LJG. Synthetic estrogen bioaccumulates and changes the behavior and biochemical biomarkers in adult zebrafish. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology. 2022;92:103857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2022.103857.
Chaulet FC, HHA Barcellos, Fior D, Pompermaier A, Koakoski G, Rosa JGS, Fagundes M, Barcellos LJG. Glyphosate- and Fipronil-Based Agrochemicals and Their Mixtures Change Zebrafish Behavior. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. 2019;77:443-451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-019-00644-7.
Barcellos HHA, Pompermaier A, Mendonça-Soares S, Maffi VC, Fernandes M, Koakoski G, Kirsten K, Baldisserotto B, Barcellos LJG. Aripiprazole prevents stress-induced anxiety and social impairment, but impairs antipredatory behavior in zebrafish. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 2020;189:172841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2019.172841.
Giacomini ACVV, Abreu MS, Giacomini LV, Siebel AM, Zimerman FF, Rambo CL, Mocelin R, Bonan CD, Piato AL, Barcellos LJG. Fluoxetine and diazepam acutely modulate stress induced-behavior. Behavioural Brain Research. 2016;296:301-310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2015.09.027.
Abreu MS, Koakoski G, Ferreira D, Oliveira TA, Rosa JGS, Gusso D, Giacomini ACV, Piato AL, Barcellos LJG. Diazepam and Fluoxetine Decrease the Stress Response in Zebrafish. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(7):e103232. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103232.
Quadros VA, Rosa LV, Costa FV, Koakoski G, Barcellos LJG, Rosemberg DB. Predictable chronic stress modulates behavioral and neuroendocrine phenotypes of zebrafish: Influence of two homotypic stressors on stress-mediated responses. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology. 2021;247:109030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2021.109030.
Kirsten K, Pompermaier A, Koakoski G, Mendonça-Soares S, da Costa AR, Maffi VC, Kreutz LC, Barcellos LJG. Acute and chronic stress differently alter the expression of cytokine and neuronal markers genes in zebrafish brain. Stress. 2021;24(1):107-112. https://doi.org/10.1080/10253890.2020.1724947.
Vargesson NA. Zebrafish. In: S. Barnett. Manual of Animal Technology. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 2007. p. 78-84.
Westerfield, M. The zebrafish book. A guide for the laboratory use of zebrafish (Danio rerio). 4th ed. Eugene: University of Oregon Press; 2000.
Lawrence C. Advances in Zebrafish Husbandry and Management. In: Detrich III HW, Westerfield M, Zon LI. Methods in Cell Biology. Vol 104. Oxford: Academic Press; 2011. p. 430-452.
Geisler R, Borel N, Ferg M, Maier JV, Strähle U. Maintenance of Zebrafish Lines at the European Zebrafish Resource Center. Zebrafish. 2016;13(S1):S19-S23. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2015.1205.
AFS, American Fisheries Society. Guidelines for the use of fishes in research. American Fish Society. Bethesda, 2014. 90 p.
Dametto FS, Fior D, Idalencio R, Rosa JGS, Fagundes M, Marqueze A, Barreto RE, Piato A, Barcellos LJG. Feeding regimen modulates zebrafish behavior. PeerJ. 2018;6:e5343. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5343.
Nasiadka A, Matthew DC. Zebrafish Breeding in the Laboratory Environment. ILAR Journal. 2012;53(2):161-168. https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar.53.2.161.
Duff NM, Sommerfeld RE, Litvak MK. Discriminating Sex in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Using Geometric Morphometrics. Zebrafish. 2019;16(2):207-213. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2018.1664.
McMillan SC, Géraudie J, Akimenko M-A. Pectoral Fin Breeding Tubercle Clusters: A Method to Determine Zebrafish Sex. Zebrafish. 2015;12(1):121-123. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2014.1060.
Hutter S, Penn DJ, Magee S, Zala SM. Reproductive behaviour of wild zebrafish (Danio rerio) in large tanks. Behaviour. 2010;147:641-660. https://doi.org/10.1163/000579510X12632972473944.
Pham LN, Kanther M, Semova I, Rawls JF. Methods for generating and colonizing gnotobiotic zebrafish. Nature Protocols. 2008;3(12):1862-1875. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.186.
Han J-H, Jung S-K. Toxicity Evaluation of Household Detergents and Surfactants Using Zebrafish. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering. 2021;26(1):156-164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-020-0109-3.
Nickmilder M, Carbonnelle S, House BA. House cleaning with chlorine bleach and the risks of allergic and respiratory diseases in children. Pediatric Allergy and Immunology. 2007; 18(1):27-35. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3038.2006.00487.x.
Berutti E, Angelini E, Rigolone M, Migliaretti G, Pasqualini D. Influence of sodium hypochlorite on fracture properties and corrosion of ProTaper Rotary instruments. International Endodontic Journal. 2006;39:693-699. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01134.x.
Liu D, Pellicer AM, Brüggmann A, Kiggen M, Behrens S, Good C, Straus DL, Meinelt T. Effect of water hardness/alkalinity and humic substances on the toxicity of peracetic acid to zebrafish embryos and pathogenic isolates. Aquaculture Reports. 2021;21:100900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2021.100900.
Garcia RL, Sanders GE. Efficacy of cleaning and disinfection procedures in a zebrafish (Danio rerio) facility. Journal of the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science. 2011;50(6):895-900. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3228927/.
Chang CT, Colicino EG, DiPaola EJ, Al-Hasnawi HJ, Whipps CM. Evaluating the effectiveness of common disinfectants at preventing the propagation of Mycobacterium spp. isolated from zebrafish. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology. 2015;178:45-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2015.09.008.
Ferguson JA, Watral V, Schwindt AR, Kent ML. Spores of two fish microsporidia (Pseudoloma neurophilia and Glugea anomala) are highly resistant to chlorine. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms. 2007;76(3):205-214. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao076205.
Chang CT, Amack JD, Whipps CM. Zebrafish Embryo Disinfection with Povidone-Iodine: Evaluating an Alternative to Chlorine Bleach. Zebrafish. 2016;13(S1):S-96-S-101. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2015.1229.
CFMV, Conselho Federal de Medicina Veterinária. 2017. Resolução no 1165, de 11 de agosto de 2017. Dispõe sobre Anotação de Responsabilidade Técnica e registro de profissionais e de estabelecimentos de cultivo e manutenção de organismos aquáticos. Diário Oficial da União. 2017; seção 1, p. 65. Portuguese.
Borges AC, Pereira N, Franco M, Vale L, Pereira M, Cunha MV, Amaro A, Albuquerque T, Rebelo M. Implementation of a Zebrafish Health Program in a Research Facility: A 4-Year Retrospective Study. Zebrafish. 2016;13(S1):1-12. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2015.1230.
CFMV, Conselho Federal de Medicina Veterinária. Resolução nº 1321, de 27 de abril de 2020. Institui normas sobre os documentos no âmbito da clínica médico-veterinária e dá outras providências. Diário Oficial da União. 2020; nº 79, seção 1, p. 112. Portuguese.
Oliveira TA, Idalencio R, Kalichak F, Rosa JGS, Koakoski G, Abreu MS, Giacomini ACV, Gusso D, Rosemberg DB, Barreto RE, Barcellos LJG. Stress responses to conspecific visual cues of predation risk in zebrafish. PeerJ. 2017;5:e3739. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.3739.
Abreu MS, Oliveira TA, Koakoski G, Barreto RE, Barcellos LJG. Modulation of Cortisol Responses to an Acute Stressor in Zebrafish Visually Exposed to Heterospecific Fish During Development. Zebrafish. 2018;15(3):228-233. http://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2017.1509.
Reolon GK, Melo GM, Rosa JG, Barcellos LJG, Bonan CD. Sex and the housing: Effects on behavior, cortisol levels and weight in zebrafish. Behavioural Brain Research. 2018;336:85-92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2017.08.006.
Rambo CL, Mocelin R, Marcon M, Villanova D, Koakoski G, Abreu MS, Oliveira TA, Barcellos LJG, Piato AL, Bonan CD. Gender differences in aggression and cortisol levels in zebrafish subjected to unpredictable chronic stress. Physiology & Behavior. 2017;171:50-54 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.12.032.
Soares SM, Kirsten K, Pompermaier A, Maffi VC, Koakoski G, Woloszyn M, Barreto RE, Barcellos LJG. Sex segregation affects exploratory and social behaviors of zebrafish according to controlled housing conditions. Physiology & Behavior.2020;222,112944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2020.112944.
Pompermaier A, Tamagno WA, Alves C, Barcellos LJG. Persistent and transgenerational effects of pesticide residues in zebrafish. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology. 2022;262:109461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2022.109461.
Varga ZM. Aquaculture, husbandry, and shipping at the Zebrafish International Resource Center. Methods Cell Biol. 2016;135:509-534. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mcb.2016.01.007.
Barton, CL, Johnson EW, Tanguay RL. Facility Design and Health Management Program at the Sinnhuber Aquatic Research Laboratory. Zebrafish. 13;(S1):S-39-S-43. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2015.1232.
Collymore C, Crim MJ, Lieggi C. Recommendations for Health Monitoring and Reporting for Zebrafish Research Facilities. Zebrafish. 2016;13(S1):S138-S148. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2015.1210.
Murray KN, Clark TS, Kebus MJ, Kent ML. Specific Pathogen Free - A Review of Strategies in Agriculture, Aquaculture, and Laboratory Mammals and How They Inform New Recommendations for Laboratory Zebrafish. Research in Veterinary Science. 2022;142:78-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2021.11.005.
Kent ML, Sanders JL. Important Parasites of Zebrafish in Research Facilities. In: Cartner SC, Eisen JS, Farmer SC, Guillemin KJ, Kent ML, Sanders GE. The Zebrafish in Biomedical Research - Biology, Husbandry, Diseases, and Research Applications [Internet]. 1st ed. London: Elsevier Academic Press; 2020. p. 479-94. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-812431-4.00040-3.
Silveira T, Kütter MT, Martins CMG, Marins LF, Boyle RT, Campos VF, Remião MH. First record of Clinostomum sp. (Digenea: Clinostomidae) in Danio rerio (Actinopterygii: Cyprinidae) and the implication of using zebrafish from pet stores on research. Zebrafish. 2021;18(2):139-148. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2020.1950.
Mähler M, Berard M, Feinstein R, Gallagher A, Illgen-Wilcke B, Pritchett-Corning K, Raspa M. FELASA Recommendations for the Health Monitoring of Mouse, Rat, Hamster, Guinea Pig and Rabbit Colonies in Breeding and Experimental Units. Laboratory Animals. 2014;48(3):178-192. https://doi.org/10.1177/0023677213516312.
Kent ML, Feist SW, Harper C, Hoogstraten-Miller S, Law JM, Sánchez-Morgado JM, Tanguay RL, Sanders GE, Spitsbergen JM, Whipps CM. Recommendations for Control of Pathogens and Infectious Diseases in Fish Research Facilities. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part C: Toxicology and Pharmacology. 2009;149(2):240-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.08.001.
Marancik D, Collins J, Afema J, Lawrence C. Exploring the Advantages and Limitations of Sampling Methods Commonly Used in Research Facilities for Zebrafish Health Inspections. Laboratory Animals. 2020;54(4):373-385. https://doi.org/10.1177/0023677219864616.
Oliveira TA, Koakoski G, Motta AC, Piato AL, Barreto RE, Volpato GL, Barcellos LJG. Death-associated odors induce stress in zebrafish. Hormones and Behavior. 2014;65(4):340-344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2014.02.009.
Paciorek T, Mcrobert S. Daily Variation in the Shoaling Behavior of Zebrafish Danio rerio. Current zoology. 2012;58(1):129-137. https://doi.org/10.1093/czoolo/58.1.129.
Graham C, von Keyserlingk MAG, Franks B. Zebrafish Welfare: Natural History, Social Motivation and Behaviour. Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 2018;200:13-22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applanim.2017.11.005.
Colwill RM, Creton R. Imaging Escape and Avoidance Behavior in Zebrafish Larvae. Reviews in the Neurosciences. 2011;22(1):63-73. https://doi.org/10.1515/RNS.2011.008.
Ali M K, Nicholson HL. Increasing Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Numbers in a Limited Tank Space Reduces Night-Time Fish Sleep-like State and and Induces Aggressive Behaviour. World Journal of Depression and Anxiety. 2018;1(1):1003.
Hutter S, Hettyey A, Penn DJ, Zala SM. Ephemeral Sexual Dichromatism in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ethology. 2012;118(12):1208-1218. https://doi.org/10.1111/eth.12027.
Lidster K, Readman GD, Prescott MJ, Owen SF. International Survey on the Use and Welfare of Zebrafish Danio rerio in Research. Journal of Fish Biology. 2017;90(5):1891-1905. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.13278.
Stevens CH, Reed BT, Hawkins P. Enrichment for Laboratory Zebrafish - A Review of the Evidence and the Challenges. Animals. 2021;11(3):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11030698.
Barcellos HHA, Koakoski G, Chaulet F, Kirsten KS, Kreutz LC, Kalueff AV, Barcellos LJG. The effects of auditory enrichment on zebrafish behavior and physiology. PeerJ. 2018;6:e5162. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5162.
Marchetto L, Barcellos LJG, Koakoski K, Soares SM, Pompermaier A, Maffi VC, Costa R, Silva CG, Zorzi NR, Demin KA, Kalueff AV, Barcellos HHA. Auditory environmental enrichment prevents anxiety-like behavior, but not cortisol responses, evoked by 24-h social isolation in zebrafish, Behavioural Brain Research. 2021;404:113169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113169.
Esmail MY, Astrofsky KM, Lawrence C, Serluca FC. The Biology and Management of the Zebrafish. In: Fox JG, Anderson LC, Otto GM, Pritchett-Corning KR, Whary MT. Laboratory Animal Medicine. 3rd ed. London: Academic Press - Elsevier Inc.; 2015. p.1015-1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-409527-4.00020-1.
Kent ML, Sanders JL, Spagnoli S, Al-Samarrie CE, Murray KN. Review of Diseases and Health Management in Zebrafish Danio rerio (Hamilton 1822) in Research Facilities. Journal of Fish Diseases. 2020;43(6):637-650. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.13165.
Cantas L, Sørby JRT, Aleström P, Sørum H. Culturable Gut Microbiota Diversity in Zebrafish. Zebrafish. 2012;9(1):26-37. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2011.0712.
Pressley ME, Phelan PE, Witten PE, Mellon MT, Kim CH. Pathogenesis and Inflammatory Response to Edwardsiella tarda Infection in the Zebrafish. Developmental and Comparative Immunology. 2005;29(6):501-513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2004.10.007.
Lin B, Chen S, Cao Z, Lin Y, Mo D, Zhang H, Gu J, Dong M, Liu Z, Xu A. Acute Phase Response in Zebrafish upon Aeromonas salmonicida and Staphylococcus aureus Infection: Striking Similarities and Obvious Differences with Mammals. Molecular Immunology. 2007;44(4):295-301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2006.03.001.
Kanther M, Rawls JF. Host-Microbe Interactions in the Developing Zebrafish. Current Opinion in Immunology. 2010;22(1):10-19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2010.01.006.
Runft DL, Mitchell KC, Abuaita BH, Allen JP, Bajer S, Ginsburg K, Neely MN, Withey JH. Zebrafish as a Natural Host Model for Vibrio cholerae Colonization and Transmission. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2014;80(5):1710-1717. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03580-13.
Mitchell, KC, Breen P, Britton S, Neely MN, Withey JH. Quantifying Vibrio cholerae Enterotoxicity in a Zebrafish Infection Model. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 2017;83(16):e00783-17. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00783-17.
Rongrong L, Hu X, Lü A, Song Y, Lian Z, Sun J, Sung YY. Proteomic Profiling of Zebrafish Challenged by Spring Viremia of Carp Virus Provides Insight into Skin Antiviral Response. Zebrafish. 2020;17(2):91-103. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2019.1843.
Beura, LK, Hamilton SE, Bi K, Schenkel JM, Odumade OA, Casey KA, Thompson EA, Fraser KA, Rosato PC, Filali-Mouhim A, Sekaly RP, Jenkins MK, Vezys V, Haining WN, Jameson SC, Masopust D. Normalizing the Environment Recapitulates Adult Human Immune Traits in Laboratory Mice. Nature. 2016;532(7600):512-516. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17655.
Rosshart SP, Vassallo BG, Angeletti D, Hutchinson DS, Morgan AP, Takeda K, Hickman HD, McCulloch JA, Badger JH, Ajami NJ, Trinchieri G, Villena FP-M, Yewdell JW, Rehermann B. Wild Mouse Gut Microbiota Promotes Host Fitness and Improves Disease Resistance. Cell. 2017;171(5):1015-1028.e13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.016.
Kanther M, Sun X, Mühlbauer M, MacKey LC, Flynn III EJ, Bagnat M, Jobin C, Rawls JF. Microbial Colonization Induces Dynamic Temporal and Spatial Patterns of NF-ΚB Activation in the Zebrafish Digestive Tract. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(1):197-207. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.03.042.
Galindo-Villegas J, Garciá-Moreno D, Oliveira S, Meseguer J, Mulero V. Regulation of Immunity and Disease Resistance by Commensal Microbes and Chromatin Modifications during Zebrafish Development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2012;109(39):e2605-e2614. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1209920109.
Cheesman SE, Neal JT, Mittge E, Seredick BM, Guillemin K. Epithelial Cell Proliferation in the Developing Zebrafish Intestine Is Regulated by the Wnt Pathway and Microbial Signaling via Myd88. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011;108(1):4570-4577. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1000072107.
Semova I, Carten JD, Stombaugh J, MacKey LC, Knight R, Farber SA, Rawls JF. Microbiota Regulate Intestinal Absorption and Metabolism of Fatty Acids in the Zebrafish Cell Host and Microbe. 2012;12(3):277-288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2012.08.003.
Davis DJ, Bryda EC, Gillespie CH, Ericsson AC. Microbial Modulation of Behavior and Stress Responses in Zebrafish Larvae. Behavioural Brain Research. 2016;311:219-227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.05.040.
Phelps D, Brinkman NE, Keely SP, Anneken EM, Catron TR, Betancourt D, Wood CE, Espenschied ST, Rawls JF, Tal T. Microbial Colonization Is Required for Normal Neurobehavioral Development in Zebrafish. Scientific Reports. 2017;7(1):1-13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10517-5.
Dobson GP, Letson HL, Biros E, Morris J. Specific Pathogen-Free (SPF) Animal Status as a Variable in Biomedical Research: Have We Come Full Circle? EbioMedicine. 2019;41:42-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.02.038.
Destoumieux-Garzón D, Mavingui P, Boetsch G, Boissier J, Darriet F, Duboz P, Fritsch C, Giraudoux P, Le Roux F, Morand S, Paillard C, Pontier D, Sueur C, Voituron Y. The One Health Concept: 10 Years Old and a Long Road Ahead. Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 2018;5:article 14,1-13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2018.00014.
Zinsstag J, Schelling E, Waltner-Toews D, Tanner M. From ‘One Medicine’ to ‘One Health’ and Systemic Approaches to Health and Well-Being. Preventive Veterinary Medicine. 2011;101(3-4):148-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prevetmed.2010.07.003.
WHO - World Health Organization, FAO - Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, OIE - World Organisation for Animal Health. Taking a Multisectoral, One Health Approach: A Tripartite Guide to Addressing Zoonotic Diseases in Countries. 2019. p.151.
Couto RM, Brandespim DF. A Review of the One Health Concept and Its Application as a Tool for Policy-Makers. International Journal of One Health. 2020;6(1):83-89. https://doi.org/10.14202/IJOH.2020.83-89.
Pace A, Dipineto L, Aceto S, Censullo MC, Valoroso MC, Varriale L, Rinaldi L, Menna LF, Fioretti A, Borrelli L. Diagnosis of Centrocestus formosanus Infection in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) in Italy: A Window to a New Globalization-Derived Invasive Microorganism. Animals. 2020;10(3):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030456.
Mesureur J, Vergunst AC. Zebrafish Embryos as a Model to Study Bacterial Virulence. In: Vergunst AC, O‘Callaghan D. Host-Bacteria Interactions Methods and Protocols. 1st ed. New York: Humana Press; 2014. p. 41-66. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-1261-2.
Rosowski EE, Knox BP, Archambault LS, Huttenlocher A, Keller NP, Wheeler RT, Davis JM. The Zebrafish as a Model Host for Invasive Fungal Infections. Journal of Fungi. 2018;4(4):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4040136.
Gomes MC, Mostowy S. The Case for Modeling Human Infection in Zebrafish. Trends in Microbiology. 2020;28(1):10-18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2019.08.005.
Pandey PK, Kass PH, Soupir ML, Biswas S, Singh VP. Contamination of Water Resources by Pathogenic Bacteria. AMB Express. 2014;4(1):1-16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-014-0051-x.
Leclerc H, Schwartzbrod L, Dei-Cas E. Microbial Agents Associated with Waterborne Diseases. Critical Reviews in Microbiology. 2002;28(4):371-409. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040-840291046768.
Oksanen KE, Myllymäki H, Ahava MJ, Mäkinen L, Parikka M, Rämet M. DNA Vaccination Boosts Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Protection against Mycobacterial Infection in Zebrafish. Developmental and Comparative Immunology. 2016;54(1):89-96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2015.09.001.
Orujyan D, Narinyan W, Rangarajan S, Rangchaikul P, Prasad C, Saviola B, Venketaraman V. Protective Efficacy of BCG Vaccine against Mycobacterium leprae and Non-Tuberculous Mycobacterial Infections. Vaccines. 2022;10(3):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10030390.
Hossain S, Silva BCJ, Dahanayake PS, Heo GJ. Characterization of Virulence Properties and Multi-Drug Resistance Profiles in Motile Aeromonas spp. Isolated from Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Letters in Applied Microbiology. 2018;67(6):598-605. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.13075.
Chandrarathna HPSU, Nikapitiya C, Dananjaya SHS, Wijerathne CUB, Wimalasena SHMP, Kwun HJ, Heo GJ, Lee J, Zoysa MD. Outcome of Co-Infection with Opportunistic and Multidrug Resistant Aeromonas hydrophila and A. veronii in Zebrafish: Identification, Characterization, Pathogenicity and Immune Responses. Fish and Shellfish Immunology. 2018;80:573-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.06.049.
Munoz-Price LS, Banach DB, Bearman G, Gould JM., Leekha S, Morgan DJ, Palmore TN, Rupp ME, Weber DJ, Wiemken TL. Isolation Precautions for Visitors. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology. 2015;36(7):747-58. https://doi.org/10.1017/ice.2015.67.
Devlin RH, Sundstro LF, Muir WM. Interface of Biotechnology and Ecology for Environmental Risk Assessments of Transgenic Fish. Trends in Biotechnology. 2006;24(2):89-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2005.12.008.
Magalhães ALB, Bezerra VS, Daga LAV, Pelicice FM, Vitule JRS, Brito MFG. Biotic Differentiation in Headwater Creeks after the Massive Introduction of Non-Native Freshwater Aquarium Fish in the Paraíba Do Sul River Basin, Brazil. Neotropical Ichthyology. 2021;19(03): e20014. https://doi.org/10.1590/1982-0224-2020-0147.
Magalhães ALB, Brito MFG, Silva LGM. The Fluorescent Introduction Has Begun in the Southern Hemisphere: Presence and Life-History Strategies of the Transgenic Zebrafish Danio rerio (Cypriniformes: Danionidae) in Brazil. Studies on Neotropical Fauna and Environment. 2022:1-13. https://doi.org/10.1080/01650521.2021.2024054.
ANVISA, Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária. 2018. Resolução da Diretoria Colegiada no. 222, de 28 de março de 2018. Regulamenta as Boas Práticas de Gerenciamento dos Resíduos de Serviços de Saúde e dá outras providências. Diário Oficial da União. 2018; nº 61; seção 1; p. 76. Portuguese.
CONAMA, Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente. Resolução CONAMA no 358 de 29 de abril de 2005. Dispõe sobre o tratamento e a disposição final dos resíduos dos serviços de saúde e dá outras providências. Diário Oficial da União. 2005; nº 84, seção 1, p. 63-65. Portuguese.
CTNBio, Comissão Técnica Nacional de Biossegurança. 2018. Resolução Normativa no 18, de 23 de março de 2018. Dispõe sobre a classificação de riscos de Organismos Geneticamente Modificados (OGM) e os níveis de biossegurança a serem aplicados nas atividades e projetos com OGM e seus derivados em contenção. Diário Oficial da União, 1-13. Portuguese.
CONCEA, Conselho Nacional de Controle de Experimentação Animal. Diretriz Brasileira para o Cuidado e a Utilizacão de Animais em Atividades de Ensino ou de Pesquisa Científica - DBCA. Atualiza o texto da Diretriz Brasileira para o Cuidado e a Utilização de Animais em Atividades de Ensino ou de Pesquisa Científica - DBCA. Diário Oficial da União. 2022; nº 192, seção 1, p. 10. Portuguese.
Nowik N, Podlasz P, Jakimiuk A, Kasica N, Sienkiewicz W, Kaleczyc J. Zebrafish: An Animal Model for Research in Veterinary Medicine. Polish Journal of Veterinary Sciences. 2015;18(3):663-674. https://doi.org/10.1515/pjvs-2015-0086.
Shive HR. Zebrafish Models for Human Cancer. Veterinary Pathology. 2013;50(3):468-82. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300985812467471.
Zhang Q, Dong X, Chen B, Zhang Y, Zu Y, Li W. Zebrafish as a Useful Model for Zoonotic Vibrio parahaemolyticus Pathogenicity in Fish and Human. Developmental and Comparative Immunology. 2016;55:159-68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dci.2015.10.021.
Silveira CR, Varela Junior AS, Corcini CD, Soares SL, Anciuti AN, Kütter MT, Martínez PE. Effects of Bisphenol A on Redox Balance in Red Blood and Sperm Cells and Spermatic Quality in Zebrafish Danio rerio. Ecotoxicology. 2019;28(8):913-22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-019-02091-5.
Almeida DV, Vaz B, Figueiredo MA, Varela Junior AS, Marins LF. Fluorescent Transgenic Zebrafish as a Biosensor for Growth-Related Effects of Methyl Parathion. Aquatic Toxicology. 2014;152:147-151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.04.001.
Andrade A, Pinto SC, Oliveira RS. Animais de Laboratório: Criação e Experimentação. Rio de Janeiro: Editora FIOCRUZ; 2002. 388 p. Portuguese. http://books.scielo.org.
Cruz JCA. Modelo de gestão em biotério convencional de produção de Rattus norvegicus de instituição de ensino superior privada brasileira. Universitas Ciências da Saúde. 2003; 01(02):343-362.
Fraser TWK, Khezri A, Jusdado JGH, Lewandowska-Sabat AM, Henry T, Ropstad E. Toxicant induced behavioural aberrations in larval zebrafish are dependent on minor methodological alterations. Toxicology Letters. 2017;276:62-68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.05.021.
Rodríguez I, Novoa B, Figueras A. Immune response of zebrafish (Danio rerio) against a newly isolated bacterial pathogen Aeromonas hydrophila. Fish & Shellfish Immunology. 2008;25(3):239-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2008.05.002.
Zheng F, Asim M, Lan J, Zhao L, Wei S, Chen N, Liu X, Zhou Y, Lin L. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of mannose receptor in zebra fish (Danio rerio) during infection with Aeromonas sobria. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015;16(5):10997-11012. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160510997.
Hawke JP, Kent M, Rogge M, Baumgartner W, Wiles J, Shelley J, Savolainen LC, Wagner R, Murray K, Peterson TS. Edwardsiellosis caused by Edwardsiella ictaluri in laboratory populations of Zebrafish Danio rerio. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health. 2013;25(3):171-83. https://doi.org/10.1080/08997659.2013.782226.
Scales BS, Dickson RP, Lipuma JJ, Huffnagle GB. Microbiology, genomics, and clinical significance of the Pseudomonas fluorescens species complex, an unappreciated colonizer of humans. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 2014; 27(4):927-48. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00044-14.
Moyer TR, Hunnicutt DW. Susceptibility of zebra fish Danio rerio to infection by Flavobacterium columnare and F. johnsoniae. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms. 2007;76:39-44. https://doi.org/10.3354/DAO076039.
Fogelson SB, Camus AC, Walter Lorenz W, Vasireddy R, Vasireddy S, Smith T, Brown-Elliott BA, Wallace Jr RJ, Hasan NA, Reischl U, Sanchez S. Variation among human, veterinary and environmental Mycobacterium chelonae-abscessus complex isolates observed using core genome phylogenomic analysis, targeted gene comparison, and anti-microbial susceptibility patterns. PLoS One. 2019;14(3):e0214274. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0214274.
Shah MK, Sebti A, Kiehn TE, Massarella SA, Sepkowitz KA. Mycobacterium haemophilum in Immuno compromised Patients. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2001;33(3):330-337. https://doi.org/10.1086/321894https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/33/3/330/277298.
Crim MJ, Lawrence C, Livingston RS, Rakitin A, Hurley SJ, Riley LK. Comparison of antemortem and environmental samples for zebrafish health monitoring and quarantine. Journal of the American Association for Laboratory Animal Science. 2017;56(4):412-424. PMCID: PMC5517331.
Cosma CL, Swaim LE, Volkman H, Ramakrishnan L, Davis JM. Zebrafish and frog models of Mycobacterium marinum infection. Current Protocols in Microbiology. 2006;10B.2(Supplement3):10B.2.1-10B.2.33. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471729256.mc10b02s3.
Linbo TL. Zebrafish (Danio rerio) husbandry and colony maintenance at the Northwest Fisheries Science Center. U.S. Dept. Commer., NOAA Tech. Memo. NMFS-NWFSC-100; 2009. 62p. https://repository.library.noaa.gov/view/noaa/3645.
Casebolt DB, Speare DJ, Horney BS. Care and Use of Fish as Laboratory Animals: Current State of Knowledge. Laboratory Animal Science. 1998;48(2):124-36. PMID: 10090003.
Jørgensen LG. Infection and immunity against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish & Shellfish Immunology. 2016;1(57):335-339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2016.08.042.
Alavinia SJ, Mirzargar SS, Rahmati-Holasoo H, Mousavi HE. The in vitro and in vivo effect of tannic acid on Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in zebrafish (Danio rerio) to treat ichthyophthiriasis. Jounal of Fish Diseases. 2018;41(12):1793-1802. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12886.
Astrofsky KM, Schech JM, Sheppard BJ, Obenschain CA, Chin AM, Kacergis MC, Laver ER, Bartholomew JL, Fox JG. High Mortality Due to Tetrahymena sp. Infection in Laboratory-Maintained Zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio). Comparative Medicine. 2002;52(4):363-367. PMID: 12211282.
Whipps CM, Murray KN, Kent ML. Occurrence of a myxozoan parasite Myxidium streisingeri n. sp. in laboratory zebrafish Danio rerio. Journal of Parasitology. 2015;101(1):86-90. https://doi.org/10.1645/14-613.1.
Sanders JL, Peterson TS, Kent ML. Early Development and Tissue Distribution of Pseudoloma neurophilia in the Zebrafish, Danio rerio. The Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 2014;61(3):238-46. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12101.
Caballero‐Huertas M, Soto M, Ribas L. Reviewing Pseudoloma neurophilia infections in the popular zebrafish model. Reviews in Aquaculture. 2021;13(4):1816-27. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12545.
Ortega C, Fajardo R, Enríquez R. Trematode Centrocestus formosanus infection and distribution in ornamental fishes in Mexico. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health. 2009;21(1):18-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1577/H07-022.1.
Wanlop A, Wongsawad C, Prattapong P, Wongsawad P, Chontananarth T, Chai JY. Prevalence of Centrocestus formosanus metacercariae in ornamental fish from Chiang Mai, Thailand, with molecular approach using ITS2. Korean Journal of Parasitology. 2017;55(4):445-449. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2017.55.4.445.
Iaria C, Migliore S, Macri D, Bivona M, Capparucci F, Gaglio G, Marino F. Evidence of Centrocestus formosanus (Nishigori, 1924) in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Zebrafish. 2019;16(6):522-526. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2019.1744.
Kent ML, Bishop-Stewart JK, Matthews JL, Spitsbergen JM. Pseudocapillaria tomentosa, a nematode pathogen, and associated neoplasms of zebrafish (Danio rerio) kept in research colonies. Comparative Medicine. 2002;52(4):354-358. PMID: 12211280.
Maley D, Laird AS, Rinkwitz S, Becker TS. A simple and efficient protocol for the treatment of zebrafish colonies infected with parasitic nematodes. Zebrafish. 2013;10(3):447-450. https://doi.org/10.1089/zeb.2013.0868.
Binesh CP. Mortality due to viral nervous necrosis in zebrafish Danio rerio and goldfish Carassius auratus. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms. 2013;104(3):257-260. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao02605.
Bermúdez R, Losada AP, de Azevedo AM, Guerra-Varela J, Pérez-Fernández D, Sánchez L, Padrós F, Nowak B, Quiroga MI. First description of a natural infection with spleen and kidney necrosis virus in zebrafish. Journal of Fish Diseases. 2018;41(8):1283-1294. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfd.12822.
Igbinosa IH, Igumbor EU, Aghdasi F, Tom M, Okoh AI. Emerging Aeromonas species infections and their significance in public health. The Scientific World Journal. 2012:625023. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/625023.
Li S, Jiang C, Chen H, Zhang L, Ke L, Chen X, Lin C. Pre-injection of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) tnfb Polyclonal Antibody Decreases the Mortality of Vibrio vulnificus Infected Zebrafish. Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 2021;8:article 741242,1-9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2021.741242.
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2023 Ciência Animal Brasileira / Brazilian Animal Science

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Autores que publicam nesta revista concordam com os seguintes termos:
- Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).






























