Hemoparasitos em gatos domésticos de Uberlândia, Minas Gerais, Brasil: positividade e fatores epidemiológicos
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1590/1809-6891v26e-79859EResumo
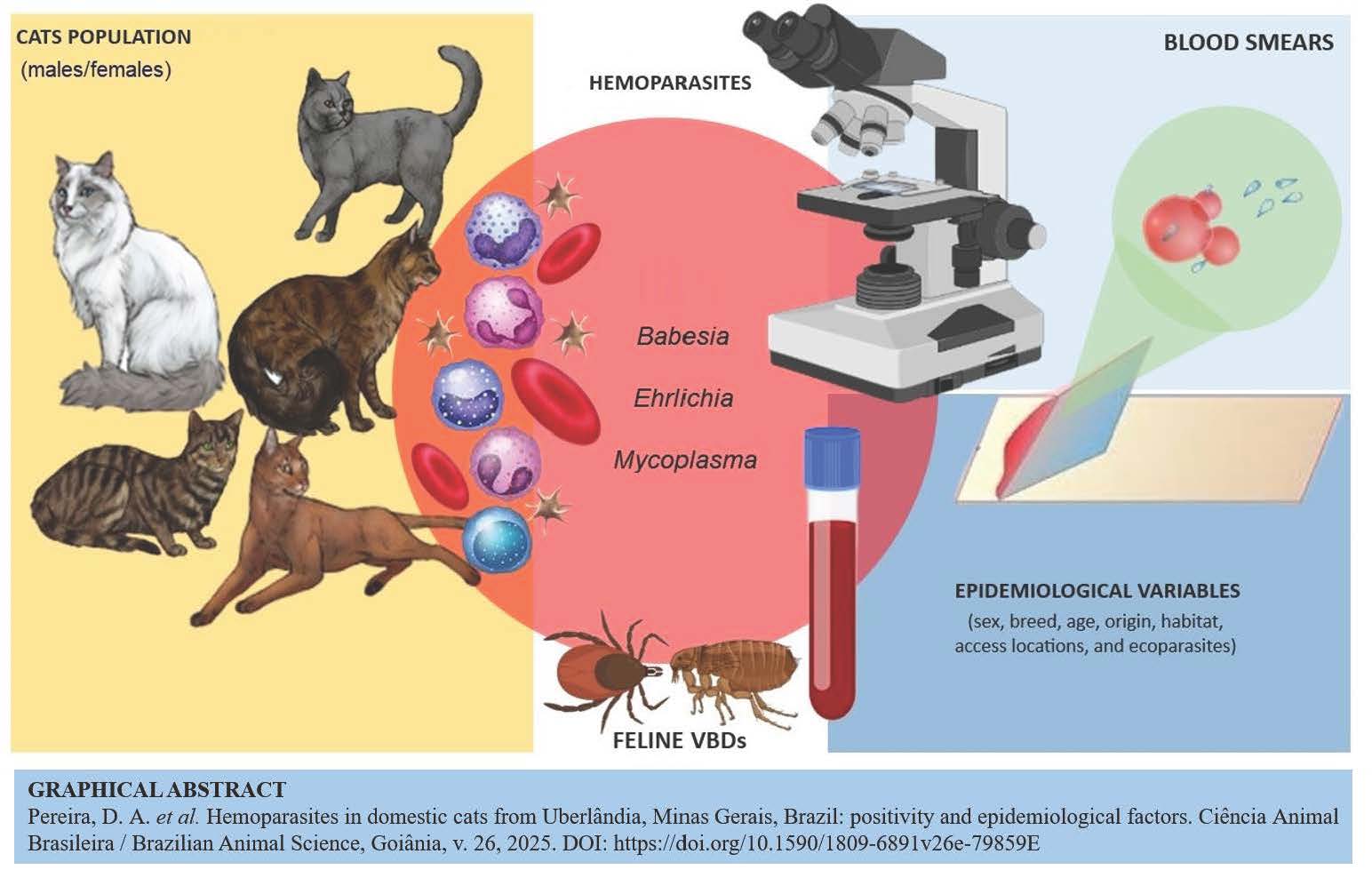
As hemoparasitose sem gatos (Felis catus) são causadas por protozoários e agentes bacterianos, transmitidos principalmente por pulgas ou carrapatos. Este estudo foi realizado para avaliar a presença de hemoparasitos em gatos domésticos da região urbana de Uberlândia (Minas Gerais, Brasil) e associar a positividade com variáveis epidemiológicas. Amostras de sangue e dados foram coletados de 300 gatos. O sangue foi obtido da ponta da orelha e duas extensões sanguíneas foram preparadas para cada animal. Informações sobre sexo, raça, idade, origem, habitat, acesso a ambientes externos, presença de ectoparasitos, dieta e região de origem também foram coletadas. Nas extensões sanguíneas, as taxas de positividade foram de 3,66% para Babesia spp., 5,33% para Ehrlichia spp. e 1,33% para Mycoplasma spp. Infecções concomitantes foram observadas entre Babesia spp. e Ehrlichia spp. (0,66%) e Babesia spp. e Mycoplasma spp. (0,33%). Habitat, acesso a ambientes externos e região de origem foram identificados como fatores significativos para a ocorrência de hemoparasitoses. Embora a maioria dos gatos amostrados vivesse em casas (66,66%), a maioria tinha livre acesso a áreas externas (81,00%), aumentando sua exposição a ectoparasitas e, consequentemente, hemoparasitos. Entre as regiões da cidade, a maior taxa de positividade (3,33%) foi observada na região leste, potencialmente ligada à menor probabilidade de os tutores dessa área manterem seus gatos estritamente dentro de casa, provavelmente influenciados por fatores socioeconômicos e culturais.
Downloads
Referências
Ayoob AL, Prittie J, Hackner SG. Feline babesiosis. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care., 2010;20(01):90-97. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-4431.2009.00493.x
Pennisi MG, Hofmann-Lehmann R, Radford AD, Tasker S, Belák S, Addie DD, Boucraut-Baralon C, Egnerink H, Frymus T, Gruffydd-Jones T, Hartmann K, Horzinek MC, Hosie MJ, Lloret A, Lutz H, Marcilio F, Thiry E, Truyen U, Möstl K. Anaplasma, Ehrlichia and Rickettsia species infections in cats: European guidelines from the ABCD on prevention and management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2017;19:542–548. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1098612X17706462
Wang JL, Li TT, Liu GH, Zhu XQ, Yao C. Two Tales of Cytauxzoon felis Infections in Domestic Cats. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017;30(04):861-885. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/cmr.00010-17
Tasker S, Hofmann-Lehmann R, Belák S, Frymus T, Addie DD, Pennisi MG, Boucraut-Baralon C, Egberink H, Hartmann K, Hosie MJ, Lloret A, Marsilio F, Radford AD, Thiry E, Truyen U, Möstl K. Haemoplasmosis in cats: European guidelines from the ABCD on prevention and management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2018;20(03):256-261. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1177%2F1098612X18758594
Baneth G, Allen K. Hepatozoonosis of dogs and cats. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2022;52(06):1341-1358. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvsm.2022.06.011
Alvarado-Rybak M, Solano-Gallego L, Millán J. A review of piroplasmid infections in wild carnivores worldwide: importance for domestic animal health and wildlife conservation. Parasit. Vectors 2016;09(01):01-19. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-016-1808-7
Lloret A, Addie DD, Boucraut-Baralon C, Egberink H, Frymus T, Gruffydd-Jones T, Hartmann K, Horzinek MC, Hosie MJ, Lutz H, Marsilio F, Pennisi MG, Radford AD, Thiry E, Truyen U, Möstl K. Cytauxzoonosis in cats: ABCD guidelines on prevention and management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2015;17:637–641. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1098612X15589878
Schäfer I, Kohn B. Anaplasma phagocytophilum infection in cats: A literature review to raise clinical awareness. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2020;22:428–441. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1098612X20917600
Penzhorn BL, Oosthuizen MC. Babesia Species of Domestic Cats: Molecular Characterization Has Opened Pandora’s Box. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020;07:134. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2020.00134
André MR, Calchi AC, Furquim MEC, De Andrade I, Arantes PVC, Lopes LCM, Demarchi IKLN, Figueiredo MAP, Lima CAP, Machado RZ. Molecular detection of tick-borne agents in cats from Southeastern and Northern Brazil. Pathogens 2022;11(01):106. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010106
Lloret A, Addie DD, Boucraut-Baralon C, Egberink H, Frymus T, Jones-Gruffydd T, Hartmann K, Horzinek MC, Hosie MJ, Lutz H, Marsilio F, Pennisi MG, Radford AD, Thiry E, Truyen U, Möstl K. Hepatozoonosis in cats: ABCD guidelines on prevention and management. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2015;17:642–644. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/1098612X15589879
Maia C, Ramos C, Coimbra M, Bastos F, Martins Â, Pinto P, Nunes M, Vieira ML, Cardoso L, Campino L. Bacterial and protozoal agents of feline vector-borne diseases in domestic and stray cats from southern Portugal. Parasit. Vectors 2014;07:01-08. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-7-115
Dantas-Torres F; Otranto D. Dogs, cats, parasites, and humans in Brazil: opening the black box. Parasit. Vectors 2014;07:01-25. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-7-22
Otranto D, Dantas-Torres F, Fourie JJ, Lorusso V, Varloud M, Gradoni L, Drake J, Geurden T, Kaminsky R, Heckeroth AR, Schunack B, Pollmier M, Beugnet F, Holdsworth P. World Association for the Advancement of Veterinary Parasitology (WAAVP) guidelines for studies evaluating the efficacy of parasiticides in reducing the risk of vector-borne pathogen transmission in dogs and cats. Vet. Parasitol. 2021;290:109369. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2021.109369
Mendes-De-Almeida F, Faria MCF, Branco AS, Serrão ML, Souza AM, Almosny N, Chame M, Labarthe N. Sanitary conditions of a colony of urban feral cats (Felis catus Linnaeus, 1758) in a zoological garden of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. São Paulo 2004;46:269-274. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/S0036-46652004000500007
Brown HM, Latimer KS, Erikson LE, Cashwell ME, Britt JO, Peterson DS. Detection of persistent Cytauxzoon felis infection by polymerase chain reaction in three asymptomatic domestic cats. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2008;20(04):485-488. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/104063870802000411
Vieira RFDC, Biondo AW, Guimarães AMS, Santos APD, Santos RPD, Dutra LH, Diniz PPVP, De Morais HA, Messick JB, Labruna MB, Vidotto O. Ehrlichiosis in brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2011;20:01-12. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-29612011000100002
Braga ÍA, Santos LGFD, Ramos DGDS, Melo ALT, Mestre GLDC, Aguiar DMD. Detection of Ehrlichia canis in domestic cats in the central-western region of Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2014;45:641-645. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822014000200036
Feitosa FLF. Semiologia veterinária: a arte do diagnóstico. 3st ed. São Paulo (Brazil): Roca Editora, 2014.
De Oliveira TYO, Hiura E, Rossi GAM, Soares FEF, Braga FR, Dos Santos PHD. Research of Hemoparasites in Domestic Cats, from Non-Governmental Organizations, in the State of Espírito Santo. Ens. Ciênc.: Ciênc. Biol. Agrár. Saúde. 2023;27(4):454-458. Doi: https://doi.org/10.17921/1415-6938.2023v27n4p454-458
Lempereur L, Beck R, Fonseca I, Marques C, Duarte A, Santos M, Zúquete S, Gomes J, Walder G, Domingos A, Antunes S, Baneth G, Silaghi C, Homan P, Zintl A. Guidelines for the detection of Babesia and Theileria parasites. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017;17(1):51-65. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2016.195
Biondo AW, Dos Santos AP, Guimarães AMS, Vieira RFC, Vidotto O, Macieira DB, Almosny NRP, Molento MB, Timenetsky J, De Morais HA; González FHD, Messick JB. A review of the occurrence of hemoplasmas (Hemotrophic mycoplasmas) in Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2009;18:1-7. Doi: https://doi.org/10.4322/rbpv.01803001
Raimundo JM, Guimarães A, Rodrigues RB, Botelho CFM, Peixoto MP, Pires MS, Machado CH, Santos HA, Massard CL, André MR, Machado RZ, Baldani CD. Hematological changes associated with hemoplasma infection in cats in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2016;25:441–449. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-29612016086
Mylonakis ME, Schreeg M, Chatzis MK, Pearce J, Marr HS, Saridomichelakis MN, Birkenheuer AJ. Molecular detection of vector-borne pathogens in Greek cats. Ticks and tick-borne Dis. 2018;9(2):171-175. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2017.08.013
Sasaki H, Ichikawa Y, Sakata Y, Endo Y, Nishigaki K, Matsumoto K, Inokuma H. Molecular survey of Rickettsia, Ehrlichia, and Anaplasma infection of domestic cats in Japan. Ticks and tick-borne Dis. 2012;3(5-6):308-311. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2012.10.028
André MR, Calchi AC, Furquim MEC, Andrade I, Arantes PVC, Lopes LCM, Demarchi IKLN, Figueiredo MAP, Lima CAP, Machado RZ. Molecular detection of tick-borne agents in cats from Southeastern and Northern Brazil. Pathogens. 2022;11(1):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11010106
Carvalho SF, Pádua GT, Paula WVF, Tavares MA, Neves LC, Pereira BG, Santos RA, Dos Santos GC, Cardoso ERN, Qualhato AF, Bitterncourt RBM, De Lima NJ, Martins DB, Dantas-Torres F, Krawczak FS. Feline Vector-Borne Diseases and Their Possible Association with Hematological Abnormalities in Cats from Midwestern Brazil. Microorganisms. 2024;12(11):2171. Doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12112171
Malheiros J, Costa MM, Do Amaral RB, De Sousa KCM, André MR, Machado RZ, Vieira MIB. Identification of vector-borne pathogens in dogs and cats from Southern Brazil. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2016;7(5):893-900. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2016.04.007
De Oliveira CM, Yang S, Duarte MA, Figueiredo DM, Batista LMR, Marr H, McManus CM, André MR, Birkenheuer AM, Paludo GR. Piroplasmid infection is not associated with clinicopathological and laboratory abnormalities in cats from Midwestern Brazil. Parasitol. Res. 2022;121(9):2561-2570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-022-07602-8
Fenelon ACg, Da Hora AS, Da Silva KL. De Oliveira GHB, Gonçalves MSS, Pastor FM, Barbosa FC, Siqueira MTS, Rosalinski-Moraes F. Co-infection of Cytauxzoon felis, Mycoplasma haemofelis, and the feline immunodeficiency virus in a domestic cat in Uberlândia, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci. 2023;60:e210131-e210131. Doi: https://doi.org/10.11606/issn.1678-4456.bjvras.2023.210131
Barbosa COS, Garcia JR, Fava NMS, Pereira DA, Da Cunha MJR, Nachum-Biala Y, Cury MC, Baneth G. Babesiosis caused by Babesia vogeli in dogs from Uberlândia State of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Parasitol. Res. 2020;119:1173-1176. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-019-06515-3
Moraes-Filho J, Krawczak FS, Costa FB, Soares JF, Labruna MB. Comparative evaluation of the vector competence of four South American populations of the Rhipicephalus sanguineus group for the bacterium Ehrlichia canis, the agent of canine monocytic ehrlichiosis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0139386. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139386
Díaz-Regañón D, Villaescusa A, Ayllón T, Rodríguez-Franco F, García-Sancho M, Agulla B, Sainz Á. Epidemiological study of hemotropic Mycoplasmas (hemoplasmas) in cats from central Spain. Parasit. Vectors 2018;11(1):140. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-2740-9
Woods JE, Brewer MM, Hawley JR, Wisnewski N, Lappin MR. Evaluation of experimental transmission of ‘Candidatus Mycoplasma haemominutum’ and Mycoplasma haemofelis by Ctenocephalides felis to cats. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2005;66(6):1008-12. Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.2460/ajvr.2005.66.1008
Tasker S. Haemotropic mycoplasmas: what's their real significance in cats? J. Feline Med. Surg. 2010;12:369–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfms.2010.03.011
Otranto D, Dantas-Torres F. Canine and feline vector-borne diseases in Italy: current situation and perspectives. Parasit. Vectors 2010;3:1-12. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-3-2
Persichetti MF, Pennisi MG, Vullo A, Masucci M, Migliazzo A, Solano-Gallego L. Clinical evaluation of outdoor cats exposed to ectoparasites and associated risk for vector-borne infections in southern Italy. Parasit. Vectors 2018;11:01-11. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-2725-8
Lappin MR. Update on flea and tick associated diseases of cats. Vet. Parasiol. 2018;254:26-29. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2018.02.022
Dos Santos, AP, Conrado FO, Messick JB, Biondo AW, De Oliveira ST, Guimaraes AMS, Do Nascimento NC, Pedralli V, Lasta CS, González FHD. Hemoplasma prevalence and hematological abnormalities associated with infection in three different cat populations from Southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2014;23(04):428-434. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-29612014079
Bergmann M, Hartmann K. Vector-borne diseases in cats in Germany. Tierarztl. Prax. Ausg. Klientiere Heimtiere 2017;45(05):329-335. Doi: https://doi.org/10.15654/TPK-160874
Arruda IF, Mendes YAC, Bonifácio TF, Gonçalves IMS, Millar PR, Barbosa AS, Abboud LCS, Amendoeira MRR. Socioeconomic profile, animal care, sanitary practices, and knowledge about parasites among owners of domestic dogs and cats treated in Rio de Janeiro city. Braz. J. Vet. Med. 2022;44. Doi: https://doi.org/10.29374/2527-2179.bjvm001822
Downloads
Arquivos adicionais
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2025 Ciência Animal Brasileira / Brazilian Animal Science

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Autores que publicam nesta revista concordam com os seguintes termos:
- Autores mantém os direitos autorais e concedem à revista o direito de primeira publicação, com o trabalho simultaneamente licenciado sob a Licença Creative Commons Attribution que permite o compartilhamento do trabalho com reconhecimento da autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm autorização para assumir contratos adicionais separadamente, para distribuição não-exclusiva da versão do trabalho publicada nesta revista (ex.: publicar em repositório institucional ou como capítulo de livro), com reconhecimento de autoria e publicação inicial nesta revista.
- Autores têm permissão e são estimulados a publicar e distribuir seu trabalho online (ex.: em repositórios institucionais ou na sua página pessoal) a qualquer ponto antes ou durante o processo editorial, já que isso pode gerar alterações produtivas, bem como aumentar o impacto e a citação do trabalho publicado (Veja O Efeito do Acesso Livre).
Declaração de dados
-
Os dados de pesquisa estão contidos no próprio manuscrito






























