DOI:
10.1590/1809-6891v20e-51187
ZOOTECNIA
PRODUCTIVE PERFORMANCE OF PRE-WEANED CALVES REARED IN THE
PANTANAL
DESEMPENHO DE BEZERROS SUBMETIDOS A DESMAMA PRECOCE NO PANTANAL
Luiz Orcirio Fialho de Oliveira1* - ORCID - http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4831-2279
Urbano Gomes Pinto de Abreu2 ORCID - http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9598-701X
Rodrigo da Costa Gomes1 ORCID - http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8410-7216
Ériklis Nogueira2 ORCID - http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7931-455X
Juliana Correa Borges Silva2 ORCID - http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5526-1828
Tereza Gabriela Costa3 ORCID - http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9348-8188
1EMBRAPA Gado de Corte, Campo Grande, MS, Brasil.
2EMBRAPA Pantanal, Corumbá, MS, Brasil.
3Universidade Federal do Mato Grosso do Sul, Campo Grande, MS,
Brasil.
*Autor para correspondência - luiz.orcirio@embrapa.br
Abstract
Early weaning (EW) has been adopted in cattle breeding farms in Pantanal
as a strategy to increase the rate of pregnancy in cows. The primary
income of these properties is the production of beef calves, and the price
of these animals depends on their weight. Therefore, the calves subjected
to EW should present weight similar to or higher than those of calves
subjected to conventional weaning (CW). This study aimed to evaluate the
productive performance of pure (Nellore) calves and crossbred
(Nellore/Angus) calves reared in the Pantanal and subjected to either EW
or CW. After EW, the calves were supplemented with concentrate at 1
kg/animal/day (low-energy diet) or 1% of live weight (high-energy diet).
The weights adjusted to 300 days of age were higher for EW calves fed the
high-energy diet (p<0.01) in both genetic groups. No significant
differences were observed in the weight of EW animals fed the low-energy
diet and CW animals (p>0.01), and animal weight was 241.17 and 236.27
kg in crossbred calves and 184.44 and 189.78 in Nellore calves,
respectively. The EW adopted in this experimental model did not affect the
productive performance of calves raised in the Pantanal.
Keywords: Nutrition, beef calves, supplementation.
Resumo
A desmama precoce (DP) vem sendo adotada nas fazendas de cria do Pantanal
como alternativa para o aumento dos índices de concepção das vacas. A
principal receita dessas propriedades são os bezerros (as), sendo o seu
valor dependente dos seus respectivos pesos. Assim é necessário que os
bezerros submetidos à DP, apresentem pesos semelhantes ou acima dos
bezerros desmamados convencionalmente. Desta forma o estudo teve como
objetivo, acompanhar o desempenho de bezerros nascidos no Pantanal,
submetidos à DP ou a desmama convencional (DC), puros (Nelore) ou Cruzados
(Nelore/Angus). Após a DP os animais receberam suplemento específico para
bezerros, na quantidade fixa de 1 kg/animal/dia (baixa energia) ou ao
nível de 1% do Peso Vivo (alta energia). Os pesos ajustados aos 300 dias
de idade foram maiores para os bezerros de DP sob alta energia
(P<0,01), em ambos os grupos genéticos. Os pesos dos animais de DP de
baixa energia e de DC, não se diferiram (P>0,01), sendo de 241,17 e
236,27 kg para o grupo de bezerros Cruzados e de 184,44 e 189,78 para o
grupo de bezerros Nelore respectivamente. A DP adotada no modelo
experimental não prejudicou o desempenho dos bezerros nascidos no
Pantanal.
Palavras-chave: Nutrição, bezerros de corte,
suplementação.
Received on: January, 23th, 2018.
Accepted on: November, 21th, 2018.
Introduction
The Pantanal biome in Brazil is a partially and temporarily flooded plain. This biome is located in the states of Mato Grosso (MT) and Mato Grosso do Sul (MS) and is affected by the floods of the rivers of the Upper Paraguay Basin. The primary economic activity in the region is the production of beef calves, and this activity has been exploited sustainably for more than two centuries(1). The cattle herd in Pantanal is composed of approximately 3.86 million animals(2), representing approximately 6.7% of the local herd (MT and MS) and 1.8% of the national herd(3).
The Pantanal plains used for extensive cattle ranching have large pasture fields; however, their low productivity and nutritional quality compromise animal performance and fertility. Conventional weaning (CW) traditionally used in Pantanal is performed from the age of 240 days and leads to a considerable loss of weight and fertility of breeding cows under conditions of nutritional restriction.
Studies on EW found no significant differences in the weight of calves subjected to either EW or CW(3,4). Besides increasing rates of conception (pregnancy) in beef cows, EW did not impair the performance of calves(5,6). With respect to the economic benefits of EW in the Pantanal, a financial return of USD 1.70 was estimated for every USD 1.00 spent(7). The estimated annual production of calves in the Pantanal is 1.10 million animals(2) and may be increased to 1.32 or even 1.54 million animals if weaning rates increase by 10% or 20%, respectively.
According to studies carried out in the region, the performance of pre-weaned calves supplemented with concentrate (1.0 kg per animal/day) for up to 100 days was not compromised compared to calves subjected to CW(4); therefore, the supply of 1.0 kg/animal/day met the nutritional requirements for productive performance to the same extent of maternal breastfeeding and provided a positive return on investment (ROI).
Nonetheless, the performance of calves supplemented with more than 1 kg/animal/day under the pasture conditions of the Pantanal is not known. In addition, the increase in weight gain in calves may help reduce the fattening time and slaughter age of the animals(8), with positive effects on enteric methane emission levels per kg of beef produced.
This study aimed to evaluate the productive performance of Nellore and Nellore-Angus calves receiving different levels of supplementation during EW.
Materials and Methods
The study was conducted at Fazenda São Bento do Abobral, located in the sub-region of Abobral (19°28'47'' S and 57°00'55'' W), city of Miranda - MS, Brazil, from January 7 to June 3, 2016. The local climate is tropical sub-humid type (Aw) according to Köppen’s classification. The study was approved by the Research Animal Ethics Committee of Embrapa Beef Cattle (Protocol Nº 002/2015).
The animals were kept in pasture lands containing a mixture of quicuio-da-Amazônia or koronivia grass (Brachiaria humidicola (Rendle) Schweick) and native forage grass [predominantly mimosa grass (Axonopus purpusii), brownseed paspalum (Paspalum plicatulum), carandazal grass (Panicum laxum), and knotroot bristlegrass (Setaria geniculata)] in the lower areas of the biome (bay margins, ebbs, and floodplains).
EW was evaluated using a factorial arrangement with two breeds [Nellore or crossbred (50% Angus and 50% Nellore)] and two supplementation diets [high-energy (HE) and low-energy (LE)].
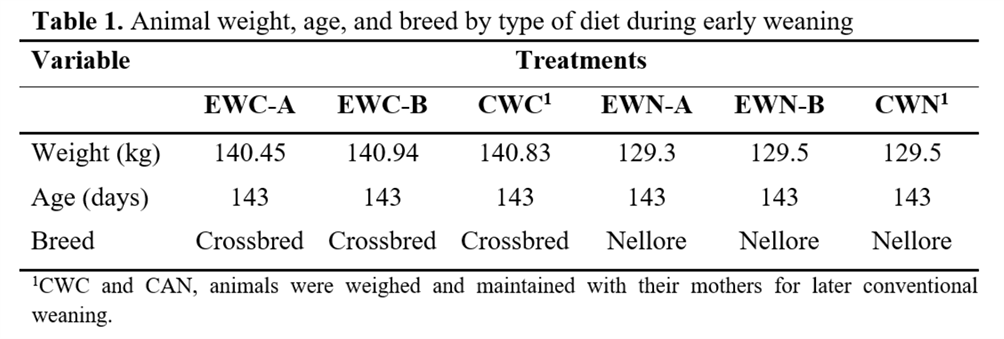
From a total of 300 calves, 180 (90 crossbred and 90
Nellore) born in August of 2015 were chosen and distributed in six groups
to standardize age and weight between the treatments. All calves born in
the study period were produced by fixed-time artificial insemination (TAI)
and had a high genetic value (Table 1):
EWC-A (n-30): EW crossbred calves supplemented with concentrate [1% of
live weight (LW)];
EWC-B (n = 30): EW crossbred calves supplemented with concentrate (1.0 kg
per animal/day);
CWC (n = 30): CW crossbred calves not supplemented;
EWN-A (n = 30): EW Nellore calves supplemented with concentrate (1% of
LW);
EWN-B (n = 30): EW Nellore calves supplemented with concentrate (1.0
kg/animal/day);
CAN (n = 30): CW Nellore calves not supplemented.
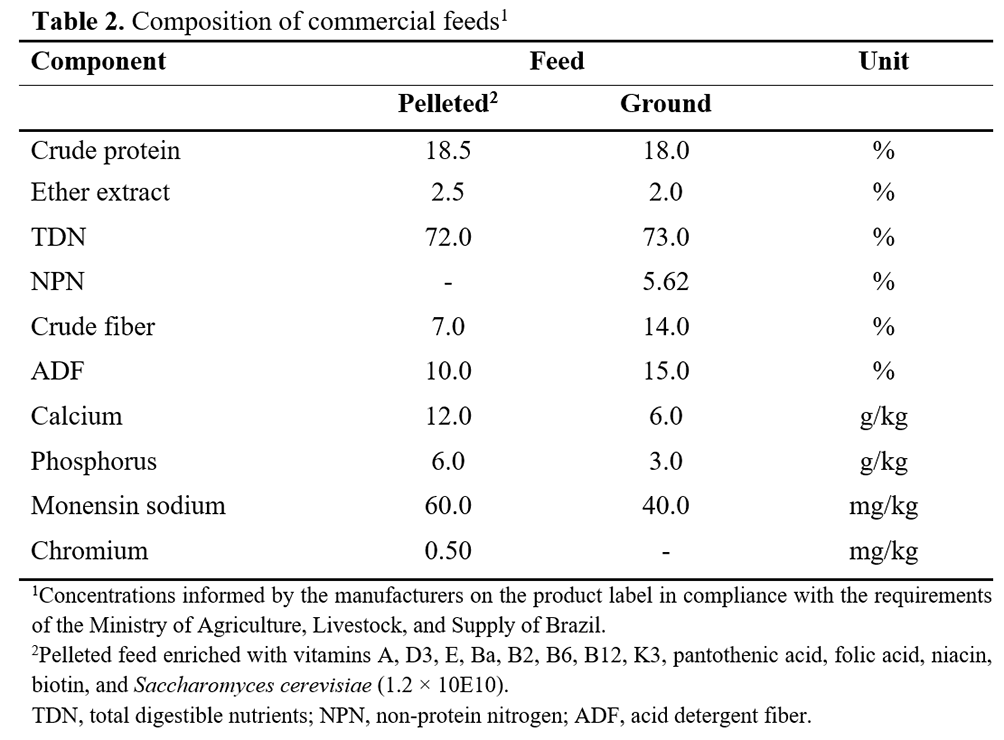
The EW animals fed an LE diet (EWC-B and EWN-B) were supplemented in the study period (January 3 to June 3, 2016) with 1.0 kg of the pelleted feed/animal/day (Table 2). For the EW animals fed an HE diet (EWC-A and EWN-A), in addition to the supply of 1 kg/animal/day of the pelleted feed, a sufficient amount of ground feed was added to reach 1% of LW. Animals subjected to CW (CWC and CAN) remained with their mothers but were not supplemented with concentrate. The supplements were offered at the same time of day (7:00 a.m.), and the leftovers were collected, weighed, and stored for further analysis and calculation of feed consumption.
The EW procedures recommended in previous studies for the region were adopted in this study(4). A methodology adapted to native pastures(9) was used for the monthly characterization of pasture, involving identifying grazing areas, measuring the distribution and frequency of forage grass species using multipliers(10,11), collecting forage to simulated grazing height, and analyzing the chemical composition of the diet(12). The animals were weighed at 56-day intervals after a 12-hour fast.
Forage and supplement samples were collected and stored in a freezer until processing. For the analyses, the samples were thawed, dried in a forced ventilation oven at 55 °C for 72 to 96 hours, and cut milled in a 1-mm sieve for chemical analysis or a 2-mm sieve for digestibility analysis(13).
After initial processing, dry matter (DM) (Method No. 930.15)(14), ether extract (Method No. 920.39)(14), mineral matter (Method No. 942.05), crude protein (CP) (Method No. 976.05)(14), neutral detergent fiber (NDF), and acid detergent fiber (ADF)(15) were measured. Degradability parameters were determined using the in situ digestibility method(16) for up to 240 hours(13), and effective degradability was adjusted using a non-linear model(17).
For data comparison, performance data (weight and weight
gain) were adjusted to 210 and 300 days of age using the following
equations because the mean age of the animals at the time of the last
weighing was 287.7 days:
PA210 = {[(FW–BW) / (DLW–DB)] × 210} + BW;
PA300 = {[(FW–BW) / (DLW-DB)] × 300} + BW, where
PA210 is the weight adjusted to 210 days of age;
PA300 is the weight adjusted to 300 days of age;
FW is the final weight (last weighing) (kg);
BW is the birth weight (kg);
DLW is the date of the last weighing (days);
DB is the date of birth (days).
With regard to the economic benefits of EW, the challenges
were considered the HE treatments (EWC-A and EWN-A) relative to
conventional LE treatments (EWC-B and EWN-B). Therefore, the return on
investment (ROI) was determined using the following equation, and the
result is shown in reais by real spent:
ROI = (P–C)/C, where
P is the profit;
C is the cost.
The final expense comprised the difference between HE supplementation minus LE supplementation costs, since other costs were assumed to be similar between treatments. The ROI was estimated by subtracting the estimated profit from the sales of the animals fed the LE diet (EWC-B and EWN-B) from the estimated profit from the sales of the animals fed the HE diet (EWC-A and EWN-A).
The sales price of the animals was estimated by the product
between the average price of the calves at auctions in the study region
(R$/kg of LW) in the reference month (June/2016)(31) and the
price of PA300.
The following equation was used:
Yij = µ + Sj + Pk + Eijk, where
Yij is the variable in animal i supplemented with j;
μ is the overall mean;
Sj is the effect of supplementation with j;
Pk is the effect of period k;
Eijk is the random error.
The study used a completely randomized block design, with a factorial for supplementation levels and genetic groups, with 30 replicates and three weighing intervals per treatment. The data were subjected to statistical analysis using the GLIMMIX procedure of the SAS software version 9.1(18).
Results and Discussion
No significant differences (P>0.05) were verified for the distribution and frequency of forage grass species between the grazing areas; thus, despite its low nutritional value, forage diet had no significant effect on treatments. The most dominant grasses in grazing areas were quicuio-da-Amazônia, mimosa grass, brownseed paspalum, carandazal grass, and knotroot bristlegrass (Table 3).
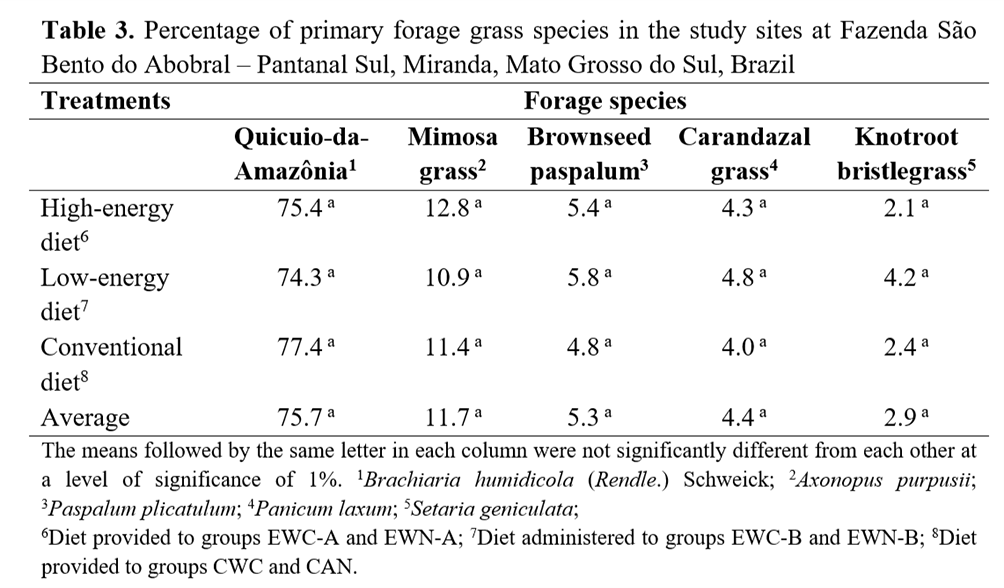
The high NDF levels in the diet (75.25%) associated with the low values of CP (below 7%), digestibility (53.19%), and energy - TDN (51.73%) may have decreased DM consumption(19) and limited the productive performance of calves (Table 4).
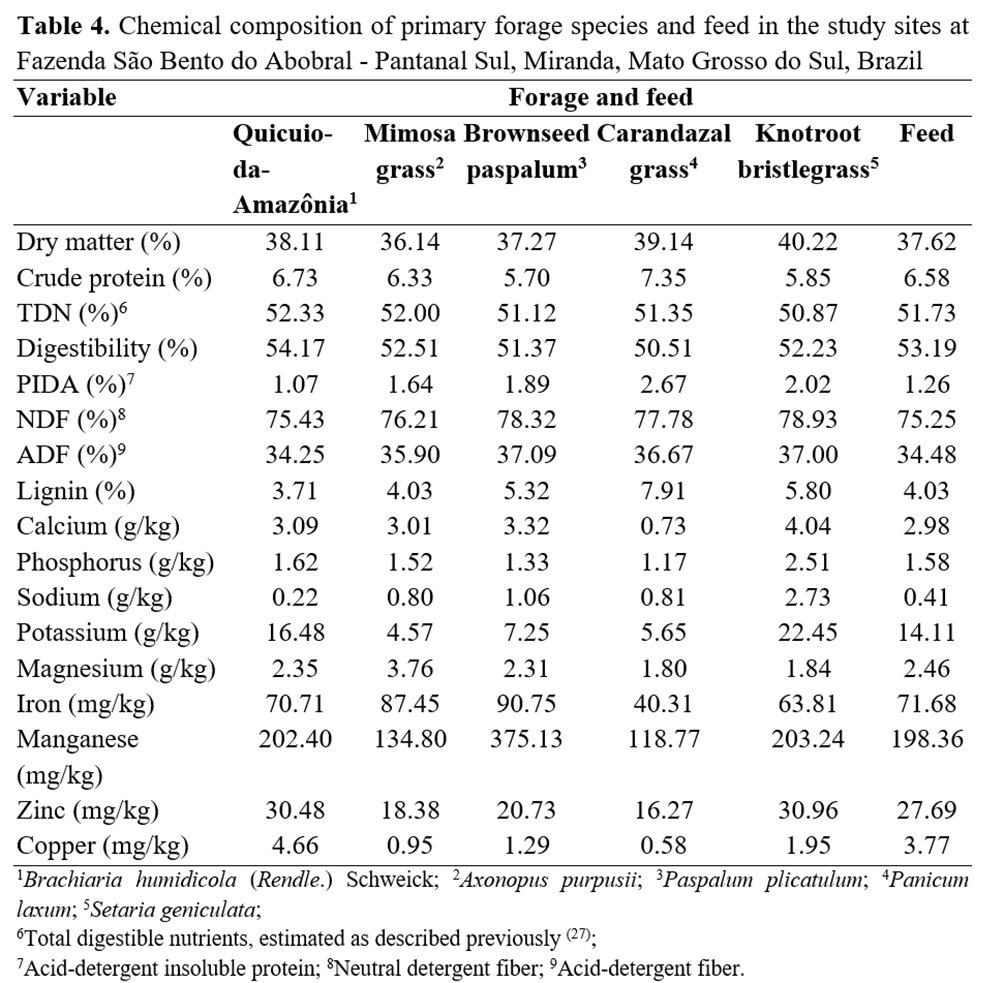
Native pastures had higher levels of indigestible protein and lower levels of digestibility when compared with cultivated pastures (quicuio-da-Amazônia). However, the chemical composition of these pastures was similar (Table 4). On the basis of mineral requirement tables, the evaluated pastures presented high levels of sodium, satisfactory levels of iron, manganese, potassium, and magnesium, and low levels of calcium, phosphorus, zinc, and copper(20).
DM consumption in animals fed LE diets is limited by the filling capacity of the digestive tract(21). Forage consumption by cattle in tropical pastures is inversely correlated with the NDF levels and was estimated at 1.27% of LW(22). Applying this percentage in the obtained NDF levels yielded an estimated DM consumption of approximately 1.68% of LW, indicating an insufficient supply of nutrients and possible limitations in productive performance(23).
Crossbred animals achieved higher weight (p<0.05) than purebred animals (Nellore) using both HE and LE diets (Table 5). The distribution of calves among treatments was balanced since all of them were the offspring of dams from the same herd, and from the same Nellore or Angus bulls. Thus, potential genetic effects on the results were mitigated, making it possible to correctly measure the effects of supplementation on performance.
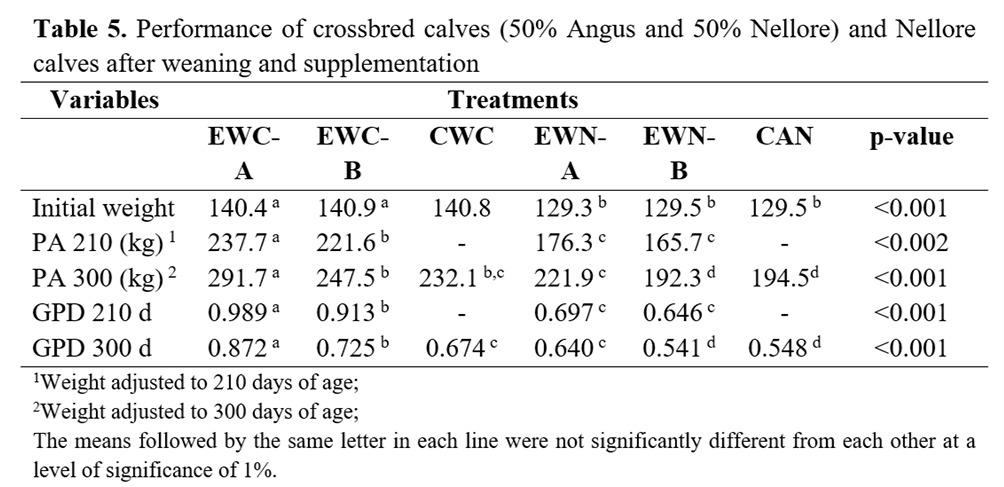
The higher performance of crossbred animals was also observed in crossbred heifers (50% Charolais and 50% Nellore) supplemented with concentrate (0.9% of LW) when compared to groups with lower levels of supplementation(26).
Crossbred animals receiving the highest amount of supplementation (EWC-A) achieved a higher weight (p<0.05) adjusted to both ages (210 and 300 days) than crossbred animals supplemented with concentrate (1.0 kg/animal/day) (EWC-B) (Figure 1). A significant difference (p<0.05) in the weight adjusted to 300 days was observed for Nellore animals, corresponding to 221.9 and 192.3 kg in animals fed the HE diet (EWN-A) and the LE diet (EWN-B), respectively.
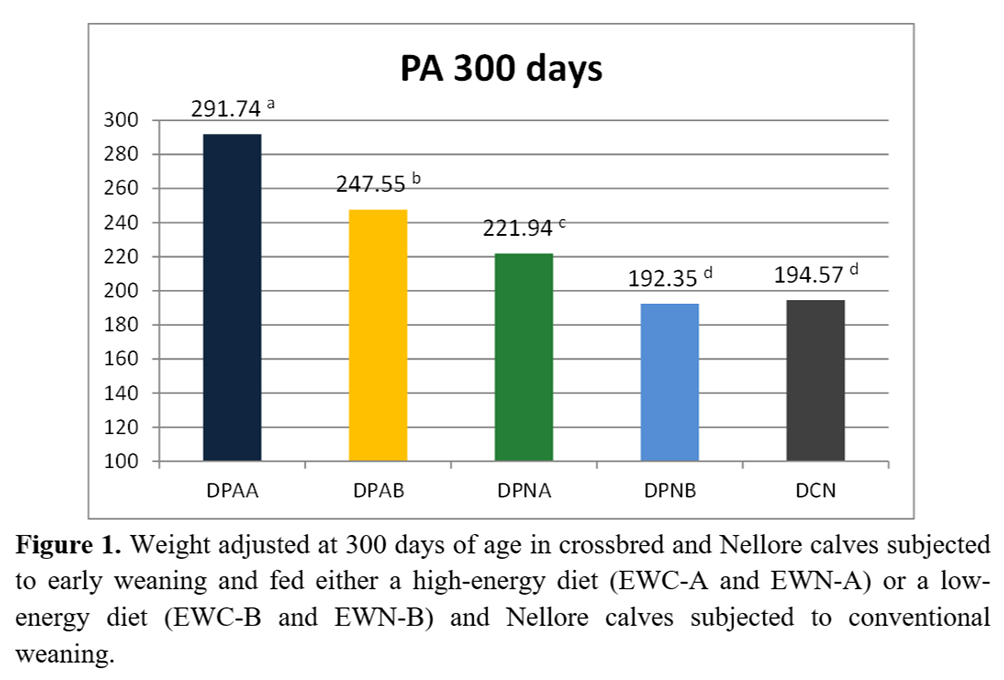
No significant difference (p>0.05) in the productive performance was verified between EW calves fed an LE diet and CW calves from the crossbred groups (247.5 and 232.1 kg for EWC-B and CWC, respectively) and between Nellore calves (192.3 and 194.5 kg for EWN-B and CAN, respectively), thus confirming the results of previous studies on EW conducted in the study region(4).
The limited nutritional value (low CP and TDN) of the diet of cows from pasture may have decreased milk production and, consequently, the productive performance of conventionally weaned calves (CAN) (Table 4).
Measuring weight gain in the first stage of life of beef cattle is fundamental for assessing the economic and environmental benefits (sustainability) of the production cycle. However, the results of supplementation of calves in creep-feeding systems are controversial, and differences in weight gain have been reported(28, 29, 30).
Furthermore, higher productive performance in the early stages of the production cycle may shorten the fattening and finishing period of steers, with economic and environmental benefits(32, 33).
The supplementation adjusted to 1% of LW in EW calves fed HE diets increased the average daily consumption per animal in 137.94 kg (279.80–141.86 kg) in crossbred calves (EWC-A and EWC-B, respectively) and 90.44 kg (223.44–133.00 kg) in Nellore calves (EWN-A and EWN-B, respectively) (Table 6). Higher supplementation (10% more) and less unconsumed feed resulted in differences in feed consumption among the genetic groups (crossbred × Nellore). Notably, the amount of feed was adjusted biweekly according to the expected weight gain, which was predicted to be 10% higher for crossbred animals.
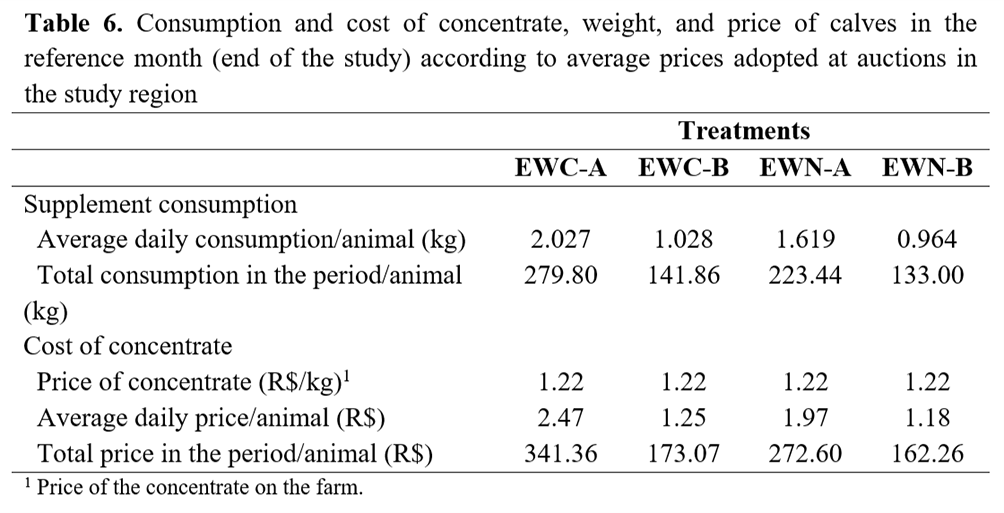
According to the analysis, in the market conditions at the time of the study, the ROI was R$ 1.63 and R$ 1.88 per real spent for animals fed the HE diet (EWC-A and EWN-A) compared to animals fed the LE diet (EWC-B and EWN-B), respectively, indicating a positive financial return (Table 7).
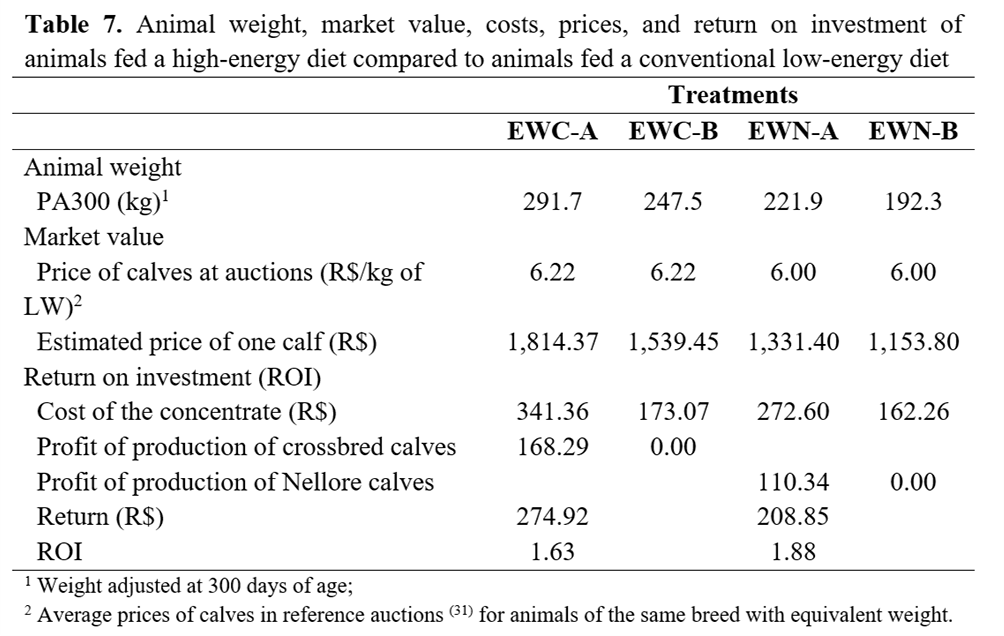
Importantly, this analysis included additional expenses and estimated revenues at the time of the study, and the results may be different in adverse situations.
Conclusions
Supplementation adjusted to 1% of the live weight of pre-weaned calves increased productive performance with economic benefits in both genetic groups studied.
Calves subjected to EW at 110 days of age may reach a weight similar to or higher than those of calves subjected to CW inasmuch as the animals are supplemented with concentrate.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Embrapa [Pre-weaning Project (Projeto + Precoce)], and the owners and employees of Fazenda São Bento do Abobral for research funding and working on this study.
References
1. Abreu UGP, Santos AS, Barros LF, Domingos IT. Pecuária
de corte e a conservação do Pantanal. Infobibos, 2008. Acessed 23 June,
2017. Available from:
http://www.infobibos.com/Artigos/2008_3/Pecuaria/index.htm.
Portuguese.
2. Oliveira LOF, Abreu UPG, Dias FRT, Fernandes FA, Nogueira E, Silva JCB.
Estimativa da população de bovinos no Pantanal por meio de modelos
matemáticos e índices tradicionais. Embrapa Pantanal – Comunicado Técnico,
2016, 99: 11p. Portuguese.
3. Waterman RC, Geary TW, Paterson JA, Lipsey RJ, Shafer WR, Berger LL,
Faulkner DB, Homm JW. Early weaning in Northern Great Plains beef cattle
production systems: III. Steer weaning, finishing and carcass
characteristics. Livestock Science, 2012; 148: 282-90.
4. Oliveira LOF, Abreu UPG, Nogueira E, Batista DSN, Silva JCB, Silva Jr.
C. Desmama precoce no Pantanal. Embrapa Pantanal – Documentos, 2014, 127:
20p. Portuguese.
5. Waterman RC, Geary TW, Paterson JA, Lipsey RJ, 2012b. Early weaning in
Northern Great Plains beef cattle production systems: II. Development of
replacement heifers weaned at 80 or 215 d of age. Livestock Science 148,
36-45.
6. Nogueira É., Abreu UGP, Oliveira LOF, Batista DSN, Mendes EDM, 2013.
Impact of the moment of TAI and rumen protected fat supplementation for
cows submitted to early weaning in native grasslands in the pantanal. 27th
Annual Meeting of the Brazilian Embryo Technology Society (SBTE),.
Proceedings of the 27th Annual Meeting of the Brazilian Embryo Technology
Society (SBTE),. Belo Horizonte: Anim. Reprod, Praia do Forte.
7. Abreu UPG, Teodoro NM, Oliveira LOF, Nogueira E, Batista, DSN. The
benefit-cost ratio and the rate of return on investiment in sustainable
intensification system of calves production in the Pantanal.2014, Annual
Meeting Brazilian Society Of Animal Science. CD-ROM, Aracaju.
8. Waterman RC, Geary TW, Paterson JA, Lipsey RJ, Shafer WR, Berger LL,
Faulkner DB, Homm JW, 2012c. Early weaning in Northern Great Plains beef
cattle production systems: III. Steer weaning, finishing and carcass
characteristics. Livestock Science 148, 282-290.
9. Santos SA, Costa C, Souza GS, JB, G, Pellegrin LA, Gutierrez R., 2002.
Metodologia de amostragens para avaliação de qualidade das pastagens
nativas consumidas por bovinos no Pantanal. Embrapa Pantanal – Documentos.
Corumbá/MS 31, 26.
10. t’Mannetje L. The dry‐weight‐rank method for the botanical analysis of
pasture. Grass and Forage Science, 1963; 18: 268-75.
11. Diogo J, Nascimento Junior D, Regazzi A. Avaliacao da composicao
botanica e da producao de materia seca de pastagens naturais utilizando-se
o botanal e outros metodos. Revista da Sociedade Brasileira de Zootecnia,
1988; 6: 578-85. Poruguese.
12. Johnson AD. Sample preparation and chemical analisys of vegetation.
Measurement of grassland vegetation and animal production., Aberustwysth:
Commonweath Agriculture Bureax, 1978, 96-102.
13. Casali AO, Detmann E, Valadares Filho SC, Pereira JC, Henriques LT,
Freitas SG, Paulino MF. Influência do tempo de incubação e do tamanho de
partículas sobre os teores de compostos indigestíveis em alimentos e fezes
bovinas obtidos por procedimentos in situ. Revista Brasileira de
Zootecnia, 2008; 37: 335-42. Portuguese.
14. AOAC. Official methods of analysis of the Association of Official
Analytical Chemists. The Association, Arlington, VA, 1990.
15. Van Soest PJ, Robertson JB, Lewis BA. Methods for dietary fiber,
neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to
animal nutrition. Journal of Dairy Science, 1991; 74: 3583-597.
16. Orskov ER, Hovell FD de B. The use of nylon bag technique for the
evaluation of feedstuffs. Trop. Anim. Prod., 1980; 5:195-223.
17. Sampaio IBM. Estatística aplicada à experimentação animal, 1st ed.
Belo Horizonte (MG): Fundação de Estudo e Pesquisa em Medicina Veterinaria
e Zootecnia, 1998, 221p. Portuguese.
18. SAS Institute. Statistical Analysis System: user guide [CD-ROM].
Version 9.1. Cary (NC): SAS Insitute Inc., 2005.
19. Egan J, Doyle P. Effect of intraruminal infusion of urea on the
response in voluntary food intake by sheep. Crop and Pasture Science,
1985; 36: 483-95.
20. McDowell LR, 1992. Minerals in animal and human nutrition. Academic
Press Inc.
21. Mertens DR. Regulation of forage intake. In: Fahey JR., GC. Forage
quality, evaluation and utilization. Winsconsin: American Society of
Agronomy, 1994. p.450-493.
22. Vásquez E. Suplementação com carboidratos não estruturais para
novilhas mestiças Holandês x Zebu em pastagem de Panicum maximum cv.
Mombaça. [master’s thesis]. [Belo Horizonte (MG)]: Universidade Federal de
Minas Gerais; 2002, 113p. Available from: http://www.capesdw.capes.gov.br/capesdw/resumo.html.
Portuguese.
23. NRC. National Research Council – NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Beef
Cattle, 7st ed. Washinton (DC): National Academy Press., 1996, 244p.
24. Perotto D, Abrahão JJS, Kroetz IA. Produtividade a Desmama de Novilhas
Nelore e F1 Bos taurus x Nelore e Bos indicus x Nelore. Revista Brasileira
de Zootecnia, 2001; 30: 1712-719. Portuguese.
25. Wolf PGL, Gregory RM, Mattos RC, Brito FV. Heterozigose individual e
materna sobre o ganho de Weight do nascimento ao desmame de terneiros
Pampiano-Braford. Ciência Rural, 1999; 29: 533-37. Portuguese.
26. Pötte, L, Rocha MG, Macari S, Roman J, Roso D, Glienke CL, Rosa ATN.
Desenvolvimento de bezerras de corte após a desmama sob níveis de
concentrado. Ciência Rural, 2010: 40: 2157-162. Portuguese.
27. Cappelle ER, Valadares Filho SC, Silva JFC, Cecon PR. Estimativas do
Valor Energético a partir de Características Químicas e Bromatológicas dos
Alimentos. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 2001; 30: 1837-856.
Portuguese.
28. Porto MO, Paulino MF, Valadares Filho SC, Detmann E, Sales MFL, Couto
VRM. Fontes de energia em suplementos múltiplos para bezerros Nelore em
creep-feeding: desempenho produtivo, consumo e digestibilidade dos
nutrientes. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 2009; 38: 1329-339.
Portuguese.
29. Nogueira E, Morais MG, Andrade VJ, Rocha EDS, Silva AS, Brito AT.
Efeito do creep feeding sobre o desempenho de bezerros e a eficiência
reprodutiva de primíparas Nelore, em pastejo. Arquivo Brasileiro de
Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia, 2006; 58: 607-613. Portuguese.
30. Forster KM, Pimentel MA, Moraes JCF. Availability of net energy in the
milk and weight performance in Hereford and Aberdeen Angus calves from
birth to weaning. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 2010; 39: 2545-552.
31. Correa da Costa Eventos Rurais LTDA. Leilão Correa da Costa. Available
from http://www.correadacosta.com.br/resultados.aspx?ano=2016&mes=6
32. Vieira A, Lobato JFP, Junior RAAT, Cezar IM, Correa ES. Recria de
machos nelore em pastagens cultivateds com suplementação na seca nos
cerrados do Brasil central. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia, 2005; 34:
1349-356. Portuguese.
33. Berndt A, Alves TC, Pedroso AF, Pezzopane JRM, Nogueira ARA, Oliveira
PPA, 2010 In Proceedings of the 5th Greenhouse Gases and Animal
Agriculture Conference. Advances in Animal Biosciences, [Cambridge],
Cambridge University Press, 2013; 4(2): 457-556. Available from http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S2040470013000113